ECU, Harness Modifications, and Sensor Wiring
Introduction to Electrical Wiring in a 2JZ Engine Swap
Swapping a 2JZ engine into a non-native car is one of the most exciting and rewarding projects for car enthusiasts, but it comes with its own set of challenges, particularly when it comes to the electrical system. While much of the focus during an engine swap is on the mechanical aspects — ensuring that the engine physically fits into the engine bay — the wiring is equally critical to ensure that the engine runs smoothly and communicates effectively with the car’s electrical system.
The electrical wiring process involves a series of steps that require precision, attention to detail, and a good understanding of how the car’s engine control unit (ECU), wiring harness, and various sensors integrate into the new engine setup. Wiring a 2JZ engine swap is not a task that should be rushed. From ECU installation to modifying or creating a custom wiring harness, each connection must be done correctly to avoid electrical issues that could cause the engine to underperform or fail entirely.
In this guide, we will walk you through everything you need to know to ensure that your 2JZ engine swap has a successful electrical setup. We’ll cover the importance of wiring, step-by-step instructions for ECU installation, wiring harness modifications, and how to wire all the sensors and components needed for the engine to perform at its best. Whether you are using a stock ECU or an aftermarket standalone ECU, this article will provide the knowledge and tools necessary for a smooth and trouble-free wiring process.
By the end of this guide, you will have a complete understanding of how to wire a 2JZ engine into your car and how to make sure it’s running optimally, with no electrical hiccups.
Understanding the Electrical Components for a 2JZ Swap
When swapping a 2JZ engine into a non-native car, understanding the key electrical components is essential for a successful installation and optimal performance. These components not only ensure that the engine runs smoothly but also help it communicate with the car’s electrical systems, such as sensors, fuel delivery, ignition systems, and more. Here’s a breakdown of the main electrical components involved in a 2JZ swap:
ECU (Engine Control Unit)
The ECU is the brain of the engine, responsible for controlling various aspects of the engine’s operation, such as fuel delivery, ignition timing, and idle speed. For a 2JZ engine swap, you’ll need to decide whether to use the stock ECU or a standalone ECU. The stock ECU may work in some cases, but often, aftermarket standalone ECUs provide more flexibility, especially if you’re modifying the engine or adding performance upgrades.
The ECU wiring involves connecting the ECU to various sensors, fuel injectors, and the ignition system. Proper integration is crucial to ensure the engine operates smoothly and efficiently.
Wiring Harness
The wiring harness is essentially the set of wires and connectors that link the engine’s electrical components (sensors, fuel system, ECU, etc.) to the car’s existing electrical system. Depending on the car and engine combination, you may need to modify an existing wiring harness or create a custom one.
- Stock Wiring Harnesses: These are often modified for a more straightforward swap when using an OEM ECU or minimal upgrades.
- Custom or Plug-and-Play Wiring Harnesses: In cases where the swap involves a different ECU or more significant changes, a custom wiring harness or plug-and-play wiring harness may be needed. These can be purchased from suppliers like Wiring Specialties, which provide pre-made wiring kits for specific swaps.
Proper installation of the wiring harness ensures that every sensor, component, and the ECU can function together without issues.
Sensors
The 2JZ engine relies on a variety of sensors to provide feedback to the ECU. These sensors monitor engine parameters such as air intake temperature, exhaust gases, crankshaft position, and throttle position. Accurate sensor readings are vital for optimal engine performance and efficiency. The main sensors you’ll deal with include:
- Crankshaft Position Sensor: Tracks the position and speed of the crankshaft, a key input for the ECU to determine timing and fuel delivery.
- Camshaft Position Sensor: Works in conjunction with the crankshaft sensor to provide additional timing data.
- Oxygen Sensors (O2): Monitors the exhaust gases to ensure the correct air-fuel ratio, enabling the ECU to adjust fuel delivery.
- Throttle Position Sensor (TPS): Measures the position of the throttle and provides input for fuel and ignition timing.
These sensors need to be wired correctly to ensure that they deliver accurate data to the ECU, which in turn controls engine behavior.
Fuel and Ignition Systems
The fuel system and ignition system are two of the most crucial systems that require wiring for a 2JZ swap. Proper wiring ensures that the fuel injectors receive the correct signal from the ECU and that the ignition coils fire at the right time. Here’s what you’ll need to wire:
- Fuel System Wiring: This includes wiring for fuel injectors, the fuel pump, and the fuel pressure regulator. If you’re upgrading to larger injectors or a high-flow fuel pump, ensure the wiring can handle the increased power demands.
- Ignition System Wiring: The ignition system relies on coil packs to ignite the air-fuel mixture in the engine. Wiring these components correctly ensures that each coil pack fires at the correct time and avoids misfires.
Grounding and Power Distribution
Grounding and proper power distribution are vital to ensure a smooth electrical setup for your 2JZ engine swap. Poor grounding can lead to electrical noise, misfires, and various other issues. You’ll need to ensure that the engine, ECU, and other components are securely grounded. Additionally, a reliable power source must be established to feed the various systems, especially if you’re using aftermarket components like a standalone ECU.
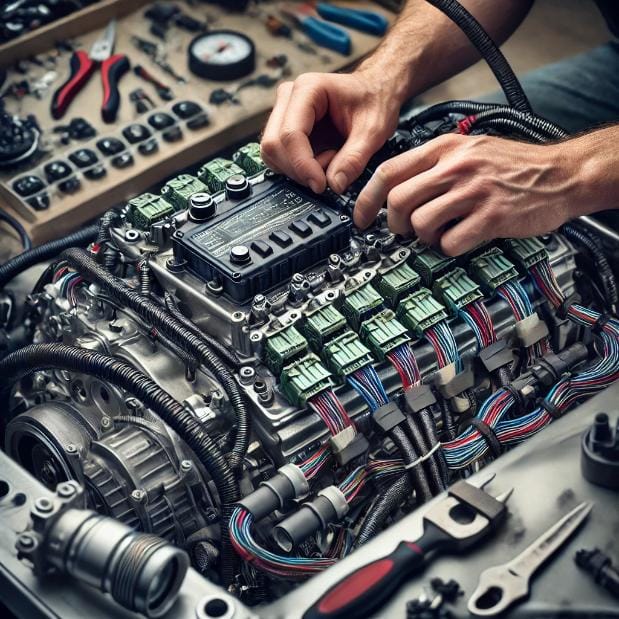

Choosing the Right ECU for a 2JZ Swap
One of the most important decisions when performing a 2JZ engine swap is selecting the ECU (Engine Control Unit). The ECU controls the entire operation of the engine, including fuel management, ignition timing, and more. Choosing the right ECU can significantly impact engine performance, tuning flexibility, and overall swap success. Let’s dive into the different ECU options for a 2JZ swap, and how to wire and integrate them into your car’s electrical system.
Types of ECUs for a 2JZ Swap
- Stock ECU (OEM ECU)
- Stock ECUs are the default choice for many engine swaps, particularly when the swap is relatively straightforward and the goal is to maintain factory-like reliability. In the case of the 2JZ, you might be able to use the OEM ECU from a Toyota Supra or Lexus IS300, depending on which 2JZ variant you are using (2JZ-GTE or 2JZ-GE).
- Pros of Using a Stock ECU:
- Easier integration with the car’s existing systems, such as the fuel pump, ignition system, and sensors.
- The stock ECU is designed specifically for the 2JZ engine, which means it’s already optimized for most of the car’s parameters.
- More affordable, as it doesn’t require purchasing an aftermarket unit.
- Cons of Using a Stock ECU:
- Limited tuning flexibility, especially for modified engines. The stock ECU is set to a certain level of performance and may not handle upgrades like a bigger turbo, bigger injectors, or custom exhaust systems.
- May require modifications to the wiring harness, and you may need an additional wiring adapter to fit the ECU to your non-native vehicle.
- Standalone ECU
- A standalone ECU is an aftermarket unit that allows for full control of the engine’s parameters, providing flexibility for performance builds and aftermarket modifications. Popular standalone ECUs for 2JZ swaps include the AEM Infinity, Haltech Platinum Pro, and Motec M1. These ECUs allow for greater tuning flexibility, including custom fuel maps, ignition maps, and the ability to support higher-performance modifications.
- Pros of Using a Standalone ECU:
- Full control over engine parameters, ideal for high-performance builds.
- The ability to modify settings for larger turbochargers, bigger injectors, and more aggressive tuning.
- Enhanced reliability and performance in modified setups, as the ECU is optimized for aftermarket upgrades.
- Cons of Using a Standalone ECU:
- More complex wiring, as you’ll need to integrate the standalone ECU into your car’s electrical system, which may require a completely new wiring harness.
- Higher cost, as standalone ECUs tend to be significantly more expensive than stock units.
- Increased tuning requirements, often needing a professional tuner to properly map the ECU for optimal performance.
- Plug-and-Play ECU
- Plug-and-play ECUs are a hybrid solution that offers some flexibility and performance enhancements of standalone ECUs while being easier to install. These ECUs are designed to fit into the stock wiring harness and make minimal modifications, providing an easier route to achieving better performance. Brands like ECUMaster and MoTeC offer plug-and-play solutions for the 2JZ engine.
- Pros of Using a Plug-and-Play ECU:
- Easier installation than a fully standalone ECU, as it can often be integrated with minimal wiring changes.
- More affordable than standalone ECUs, while still offering improved control over engine parameters.
- Good middle-ground solution for those wanting better performance and tuning flexibility without the complexity of a full standalone ECU.
- Cons of Using a Plug-and-Play ECU:
- Limited tuning options compared to fully standalone units, which may restrict modifications in the future.
- Less control over engine parameters than a full standalone ECU.
How to Wire the ECU for Your 2JZ Swap
Once you’ve chosen the right ECU for your 2JZ swap, the next challenge is wiring it into the car. The wiring process for the ECU can vary significantly depending on whether you’re using a stock ECU, a standalone ECU, or a plug-and-play unit. Below are the general steps for wiring the ECU into a non-native car:
- Wire the ECU Power and Grounding:
- The ECU requires a stable power supply and grounding to function properly. In most cases, the stock wiring harness will already have the necessary power and ground wires, but these may need to be adapted for your specific ECU.
- Connect the ECU to the Wiring Harness:
- For a stock ECU, the main task is ensuring that the wiring harness fits and that the correct pins on the ECU are connected to the corresponding components in the car, such as fuel injectors, ignition coils, sensors, etc.
- For standalone ECUs, a new custom wiring harness will likely need to be created to connect the ECU to the engine’s components. You’ll also need to connect the ECU to the car’s power source and grounding system.
- Integrate the ECU with the Sensors and Engine Components:
- Connect the ECU to key sensors such as the crankshaft position sensor, camshaft position sensor, O2 sensors, and other components that communicate engine data. This ensures that the ECU can adjust fuel delivery, ignition timing, and more based on real-time data from the engine.
- Programming and Tuning:
- After wiring, you’ll need to either upload the stock ECU’s map (if using a stock ECU) or create a custom map (if using a standalone ECU). This step is vital for ensuring that the ECU communicates effectively with the engine and car systems, allowing the engine to run at its best.
Modifying the Wiring Harness for the 2JZ Swap
When performing a 2JZ engine swap, one of the most crucial tasks is modifying the wiring harness to ensure that all electrical components in the engine bay communicate properly with the car’s existing electrical systems. Whether you are using a stock ECU or an aftermarket standalone ECU, the wiring harness needs to be tailored to connect the 2JZ engine to the various systems in your car. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to modify or create a custom wiring harness for a successful 2JZ engine swap.
Why Modify the Wiring Harness?
In most cases, the stock wiring harness from your donor vehicle will not be fully compatible with the new 2JZ engine, especially if you’re swapping into a non-native vehicle. A 2JZ engine wiring harness is designed to work with specific sensors, connectors, and ECU inputs. As a result, you may need to modify the harness to:
- Fit the sensor connectors that are specific to the 2JZ engine (such as crankshaft, camshaft, and O2 sensors).
- Adapt the wiring for the fuel injectors, ignition system, and turbo control (if applicable).
- Ensure compatibility with the new ECU, whether it’s stock or standalone.
- Integrate new components, such as boost control systems, custom fuel systems, or aftermarket ignition systems.
Types of Wiring Harness Modifications
There are two main approaches to modifying a wiring harness for your 2JZ swap:
- Modifying the Stock Harness
- This approach involves adapting the wiring from the car’s stock engine harness to the new 2JZ engine. If you’re using the stock ECU, the existing harness may only need minor adjustments, such as:
- Re-pinning connectors to match the 2JZ ECU or sensors.
- Adding or removing wires to accommodate changes in engine management.
- Extending or shortening wires for better fitment in the new engine bay.
- Pros of Modifying the Stock Harness:
- Easier and more cost-effective than building a custom harness from scratch.
- Keeps the stock car wiring intact, ensuring minimal disruption to existing systems like the dashboard, lighting, and power systems.
- Works well if you’re using a stock ECU and not making significant engine modifications.
- Cons:
- Limited flexibility for modifications like higher boost levels, larger fuel injectors, or performance tuning.
- Time-consuming process, especially if you need to locate specific diagrams and make sure everything fits.
- This approach involves adapting the wiring from the car’s stock engine harness to the new 2JZ engine. If you’re using the stock ECU, the existing harness may only need minor adjustments, such as:
- Building a Custom Wiring Harness
- If you’re going for a standalone ECU or your car’s wiring system is too different to adapt the stock harness easily, building a custom wiring harness is a better option. This allows you to start fresh with a wiring system tailored to the 2JZ engine and your specific swap configuration.
- Steps for Building a Custom Wiring Harness:
- Get the Right Wiring Diagram: Start with the 2JZ engine wiring diagram, which will show the pinouts and wiring connections for the engine sensors, ECU, and fuel system. Having an accurate diagram ensures you wire everything correctly.
- Choose Quality Wires and Connectors: Use high-quality wires rated for the current that will be running through them, especially for components like fuel injectors, ignition coils, and sensors. Also, choose weather-resistant connectors to ensure long-term durability.
- Map Out Your Connections: Lay out the wiring for each component, including engine sensors, fuel system, ignition system, and ECU. Plan where the wires will run through the engine bay and ensure they will not be in the way of moving parts or exposed to heat.
- Connect the ECU and Sensors: Wire the ECU to the sensors, such as the crankshaft position sensor, camshaft position sensor, and O2 sensors. Make sure that each sensor is correctly wired to the ECU for accurate feedback.
- Test and Secure the Wiring: Once the harness is built, make sure to test each wire for continuity. After that, secure the harness in place using zip ties or harness clamps, and ensure that all connections are clean and tight.
- Pros of Building a Custom Harness:
- Complete control over the wiring setup, ensuring it’s designed for your specific engine configuration and swap needs.
- Allows you to incorporate advanced tuning options, high-performance components, and future upgrades.
- Best for standalone ECUs and swaps into non-native vehicles.
- Cons:
- More time-consuming and labor-intensive.
- Higher cost for the required materials, such as wires, connectors, and tools.
- Requires more technical knowledge to ensure everything is wired correctly.
- Pros of Building a Custom Harness:
Key Considerations When Modifying or Creating a Wiring Harness
- Compatibility with Your Vehicle: Ensure that your wiring harness will integrate well with the car’s existing electrical systems. Some vehicles might have different voltage levels or sensor types, requiring additional modifications.
- Clearance and Durability: Make sure that the wiring harness is routed safely, away from heat sources, moving parts, or areas prone to damage. Use heat shields or insulated cables where necessary.
- Future-Proofing: If you plan to upgrade your 2JZ engine with bigger turbos, more powerful injectors, or other performance modifications, it’s a good idea to leave some extra capacity in your harness for future upgrades.
- Pinouts and Diagrams: Carefully follow 2JZ wiring diagrams to ensure proper connections and prevent mistakes that could lead to engine misfires or electrical issues.
Benefits of Using a Pre-Made Wiring Harness
If you’re looking to simplify the wiring process, many companies offer plug-and-play or pre-made wiring harnesses for 2JZ swaps. These harnesses are designed to connect your 2JZ engine to the car’s electrical system, reducing the time and complexity of wiring.
- Wiring Specialties, for example, provides standalone wiring harnesses for popular 2JZ swaps, offering an easy and reliable solution for those looking to reduce installation time and ensure proper connections.
Wiring the 2JZ Engine Sensors
The sensor wiring is one of the most critical elements of a 2JZ engine swap. Sensors provide real-time data to the ECU, allowing it to adjust various engine parameters such as fuel delivery, ignition timing, and air-fuel mixture for optimal performance. Incorrectly wired sensors or poor connections can lead to engine malfunctions, erratic performance, or complete failure. Let’s explore the key sensors in a 2JZ engine swap and how to wire them properly for a successful setup.
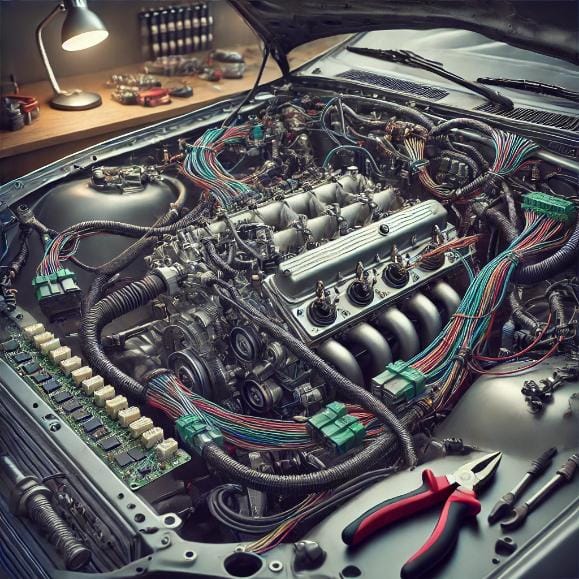
Key Sensors in a 2JZ Engine Swap
- Crankshaft Position Sensor (CKP)
- The crankshaft position sensor is one of the most essential sensors in your 2JZ swap. It monitors the position of the crankshaft and relays this data to the ECU to synchronize the ignition and fuel injection timing. Without an accurate signal from the crankshaft position sensor, the ECU cannot correctly time engine functions, resulting in poor performance or no start at all.
- Wiring the Crankshaft Position Sensor:
- Typically, the CKP sensor requires a two-wire connection: one for the signal and one for the ground. The signal wire is connected to the ECU, while the ground wire ensures proper electrical flow.
- It’s essential to route the CKP sensor wire away from other wiring that could cause electrical interference (such as high-voltage ignition or fuel injector wiring).
- Ensure the sensor is correctly mounted and aligned with the crankshaft to provide accurate readings.
- Camshaft Position Sensor (CMP)
- The camshaft position sensor works in tandem with the crankshaft position sensor to provide more precise control over fuel injection and ignition timing. It monitors the position of the camshaft, allowing the ECU to adjust timing for better performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions.
- Wiring the Camshaft Position Sensor:
- Similar to the CKP sensor, the CMP sensor typically requires two wires: a signal wire and a ground wire.
- The signal wire sends data about the camshaft’s position to the ECU, while the ground wire ensures accurate data transmission.
- Position the CMP sensor correctly to avoid incorrect readings, and ensure the wiring is secure and shielded from interference.
- Oxygen Sensors (O2 Sensors)
- Oxygen sensors are critical in managing the air-fuel ratio of the engine. The ECU uses the data from these sensors to determine whether the engine is running rich or lean. Based on this data, the ECU adjusts fuel delivery to ensure optimal combustion efficiency and emissions control.
- Wiring the Oxygen Sensors:
- Upstream (pre-catalytic converter) and downstream (post-catalytic converter) O2 sensors are typically used in a 2JZ engine swap, especially in cars with modern emissions requirements.
- These sensors have a four-wire connection: power, ground, and two signal wires (one for voltage and one for heater signal).
- Ensure proper placement of the O2 sensors in the exhaust manifold or exhaust system for accurate readings. The O2 sensor wiring should be routed in such a way that it is protected from heat, moisture, and wear.
- Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)
- The throttle position sensor is essential for monitoring the throttle body’s position and sending this information to the ECU. The ECU uses this data to adjust fuel and ignition timing based on the throttle’s input, improving responsiveness and performance.
- Wiring the Throttle Position Sensor:
- The TPS typically has a three-wire connection: one for the signal, one for ground, and one for the reference voltage (usually 5V).
- Proper calibration of the TPS is important. Ensure that it is wired correctly to avoid erroneous throttle readings, which could lead to poor idle control or sluggish engine response.
- Coolant Temperature Sensor (CTS)
- The coolant temperature sensor measures the temperature of the engine coolant and sends the data to the ECU. This information is crucial for adjusting fuel mixtures and ignition timing, especially during cold starts. If the sensor isn’t working properly or is wired incorrectly, it can cause poor performance, excessive fuel consumption, or difficulty starting the engine.
- Wiring the Coolant Temperature Sensor:
- The CTS typically has two wires: a signal wire and a ground wire.
- Ensure that the CTS wire is securely connected and shielded from other wiring to prevent erroneous signals.
- Intake Air Temperature Sensor (IAT)
- The intake air temperature sensor measures the temperature of the incoming air, providing data to the ECU that is used to adjust fuel delivery and ignition timing. The ECU needs this data to ensure that the engine is running efficiently, especially under varying atmospheric conditions.
- Wiring the Intake Air Temperature Sensor:
- The IAT sensor typically has two wires: one for the signal and one for ground.
- Ensure that the sensor is positioned in the intake manifold or air intake system and that the wiring is routed away from heat sources.
- Knock Sensor
- The knock sensor listens for signs of engine knock (pre-detonation) and sends this data to the ECU. If knock is detected, the ECU will adjust timing to protect the engine from damage.
- Wiring the Knock Sensor:
- The knock sensor typically has a two-wire connection, one for the signal and one for ground.
- Positioning the knock sensor properly and ensuring the wiring is secure and free from interference is crucial for accurate detection and engine protection.
Proper sensor wiring is paramount in ensuring that the 2JZ engine swap runs at its optimal performance. Each sensor must be wired carefully to ensure accurate feedback to the ECU, which in turn adjusts engine parameters for smooth operation and maximum power. Incorrectly wired sensors can lead to a range of issues, from poor fuel economy to severe engine damage.
Wiring the Fuel and Ignition Systems for the 2JZ Engine Swap
Wiring the fuel system and ignition system is critical for a successful 2JZ engine swap. Proper wiring ensures that the fuel injectors are delivering the correct amount of fuel to the engine and that the ignition coils are firing at the right time. Mistakes in wiring these systems can lead to misfires, poor performance, and even engine damage. In this section, we will explore the steps for wiring both systems and ensure they work together seamlessly with the 2JZ engine.
Fuel System Wiring
The fuel system consists of several components that must be correctly wired to ensure proper fuel delivery. These include the fuel injectors, fuel pump, and fuel pressure regulator. Let’s dive into the specifics of wiring each component for a 2JZ swap.
- Fuel Injectors
- The fuel injectors are responsible for delivering the right amount of fuel to each cylinder at the right time. For the 2JZ engine, whether you’re using stock injectors or upgraded units, wiring the injectors properly is essential for achieving the correct air-fuel ratio.
- Wiring the Fuel Injectors:
- Fuel injectors usually have two wires: one for the ground and one for the signal from the ECU.
- Each injector is typically wired in pairs (banks of 3 injectors for a 6-cylinder engine), and the ECU sends the signal to the injector based on the engine’s fuel needs.
- When wiring larger injectors for performance applications, ensure that the wiring can handle the increased power demand. You may need to upgrade the fuel injector harness to match the increased current.
- Key Considerations:
- Ensure that the injector wiring is routed away from heat sources and moving parts, such as the engine belts or exhaust system.
- Double-check the wiring polarity for the injectors; reversing the wires can cause fuel delivery issues.
- Fuel Pump
- The fuel pump is responsible for supplying fuel to the injectors at the proper pressure. For 2JZ swaps, especially those involving higher-performance setups, you may need to upgrade the fuel pump to ensure adequate fuel delivery.
- Wiring the Fuel Pump:
- The fuel pump wiring typically consists of two wires: one for power and one for ground. In some cases, there might also be a relay involved to control when the pump is activated.
- For performance applications, such as those running a higher fuel pressure regulator, ensure that the fuel pump is capable of supplying fuel at the increased flow rate.
- When wiring the fuel pump, ensure that the fuel lines are correctly routed and secured, as improper fuel pump wiring or installation can result in fuel leaks or insufficient fuel flow.
- Fuel Pressure Regulator
- The fuel pressure regulator controls the fuel pressure to the injectors, ensuring that they receive a consistent flow of fuel. It works in conjunction with the fuel pump and injectors to maintain the ideal pressure in the fuel system.
- Wiring the Fuel Pressure Regulator:
- The fuel pressure regulator generally has two wires: one for power and one for ground.
- Ensure that the fuel pressure regulator is connected properly to the fuel rail, fuel lines, and ECU for accurate fuel pressure control.
Ignition System Wiring
The ignition system is responsible for delivering spark to the engine at the correct timing, ensuring combustion occurs in each cylinder. Wiring the ignition system for the 2JZ swap is a critical step to ensure reliable engine operation, especially at higher performance levels.
- Ignition Coils
- The ignition coils in the 2JZ engine are responsible for generating the high voltage needed to create a spark at the spark plugs. The 2JZ-GTE uses a coil-on-plug system, meaning each cylinder has its own coil.
- Wiring the Ignition Coils:
- Each coil has three wires: one for signal (from the ECU), one for power (from the battery or relay), and one for ground.
- Ensure that the ignition coil wiring is routed in such a way that it avoids high-voltage interference from the fuel injectors or other sensors.
- Proper coil placement is essential. Ensure that each coil is securely mounted and connected to its corresponding cylinder for efficient ignition.
- Crankshaft and Camshaft Position Sensors
- As mentioned earlier, the crankshaft and camshaft position sensors provide critical timing data to the ECU, allowing it to synchronize the firing of the ignition coils and the fuel injectors.
- Wiring the Position Sensors:
- These sensors typically require two wires: a signal wire and a ground wire.
- Make sure the wiring is securely connected, and the sensors are correctly positioned on the engine to detect the correct rotation of the crankshaft and camshaft.
- Improper sensor wiring or placement can result in ignition timing errors, leading to engine misfires or failure to start.
- Spark Plugs
- The spark plugs are the final link in the ignition system, where the spark is delivered to ignite the fuel-air mixture in the cylinders. While spark plugs themselves don’t require direct wiring, the coil packs that provide the ignition voltage do.
- Wiring for Spark Plugs:
- Ensure that the coil packs are wired securely to the spark plugs. Ensure that the wires are routed properly to avoid short circuits or wear.
Key Wiring Considerations for the Fuel and Ignition Systems:
- Wire Sizing: Make sure that the wires used for the fuel and ignition systems are adequately sized for the current they will carry. Using undersized wires can lead to voltage drops, misfires, and other performance issues.
- Routing and Protection: Properly route the wiring for both the fuel system and ignition system to avoid interference with heat sources, moving parts, or areas that may cause damage. Use protective sleeves or heat-resistant tubing where necessary.
- Grounding: Proper grounding is essential to prevent electrical noise and ensure proper operation of the fuel and ignition systems. Use solid ground connections to the car’s chassis or engine block.
- Testing: After wiring the fuel and ignition systems, test the entire setup for continuity, grounding, and functionality. Verify that the injectors fire correctly, the fuel pump is delivering fuel, and the ignition system is providing spark at the right timing.
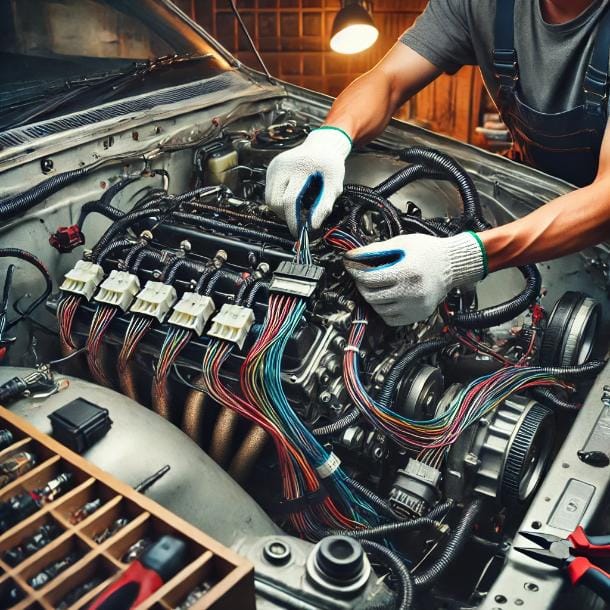

Common Wiring Mistakes and Troubleshooting
When performing a 2JZ engine swap, wiring is one of the most complex and crucial aspects of the project. Even the smallest mistake in wiring can lead to performance issues, electrical failures, or even engine damage. This section will cover some of the most common wiring mistakes people make during a 2JZ swap, how to troubleshoot wiring problems, and tips for ensuring everything is working properly.
1. Incorrect Pinouts and Miswired Connectors
One of the most frequent issues during a 2JZ engine swap is incorrect pinouts or miswired connectors. Each component in the engine’s wiring system has a specific pinout that must match the ECU, sensors, and components.
- Symptoms: Engine may not start, ECU may not communicate properly with the sensors, or components may malfunction.
- Common Causes: Confusing wire colors, misinterpreting wiring diagrams, or using the wrong connector for a specific sensor.
How to Avoid This:
- Use a reliable wiring diagram specific to the 2JZ engine and your car’s setup to ensure that each wire is connected to the correct pin.
- Double-check connector types, especially when swapping harnesses from different models or integrating a standalone ECU.
- Label connectors and wires during the installation to ensure that you can easily identify the correct connections.
2. Poor Grounding and Electrical Noise
A common wiring issue that can cause a variety of problems is poor grounding. A solid ground connection is essential for the proper functioning of the entire electrical system. Electrical noise can also interfere with sensor readings and ECU communication.
- Symptoms: Erratic engine behavior, sensors giving incorrect readings, or even misfires due to poor sensor feedback.
- Common Causes: Grounding wires not properly connected to the car’s chassis or engine block, or using insufficient gauge wire for grounding.
How to Avoid This:
- Ensure that all ground connections are made to clean, rust-free metal surfaces on the engine or chassis.
- Use thicker gauge wire for ground connections to ensure adequate current flow.
- Test ground continuity with a multimeter to ensure that all components are properly grounded.
3. Ignoring Wiring Harness Protection
Exposed or improperly routed wires can easily get damaged due to heat, friction, or contact with moving parts. This is especially important when routing wires near hot components like the exhaust manifold, alternator, or engine block.
- Symptoms: Short circuits, sparking, or blown fuses, which can cause the engine or electrical system to malfunction.
- Common Causes: Not using protective sleeves, heat-resistant tubing, or improper routing of wires near hot or moving components.
How to Avoid This:
- Use heat-resistant tubing or protective sleeves for all wires that are near heat sources or sharp edges.
- Ensure that all wiring is properly clamped or routed away from sharp objects, moving parts, and heat sources.
- Regularly inspect all wiring after installation to ensure that no wires are exposed to potential damage.
4. Incorrect Sensor Wiring or Misconnections
Incorrectly wiring sensors can lead to improper data being sent to the ECU, causing poor engine performance or an inability to start. For example, wiring the crankshaft position sensor to the wrong pin can lead to misfires or the engine not recognizing the correct timing.
- Symptoms: Poor engine idle, misfires, or no-start conditions due to the ECU receiving incorrect data from sensors.
- Common Causes: Misreading wiring diagrams, incorrect connections between sensor plugs and ECU pins, or incorrect sensor placement.
How to Avoid This:
- Cross-check all sensor wiring against the 2JZ wiring diagram to ensure accurate connections.
- Use connectors that are specifically designed for each sensor and avoid using universal connectors that might not fit properly.
- Ensure proper sensor placement, particularly for critical components like the crankshaft position sensor and camshaft position sensor.
5. Not Using the Correct Wire Gauge for High-Current Components
Using the wrong wire gauge for components that draw a lot of power—such as the fuel pump, ignition system, or starter motor—can lead to voltage drops, overheating wires, or blown fuses.
- Symptoms: Power loss, electrical components not functioning properly, or blown fuses when trying to start the engine.
- Common Causes: Using wire gauges that are too small for components that draw high current, leading to heat buildup and potential wire damage.
How to Avoid This:
- Use the appropriate wire gauge for each component based on its power requirements. Refer to the manufacturer’s specifications for each part to determine the correct wire size.
- Fuse each high-current component with the correct amperage to protect the wiring and prevent damage to sensitive electrical parts.
6. Forgetting to Test the Electrical System
Many enthusiasts rush through the wiring process and forget to test the entire electrical system before firing up the engine. This can lead to missed issues, such as incorrect pinouts, unconnected components, or faulty sensors.
- Symptoms: Engine fails to start, misfires, or components like the fuel system or ignition coils do not operate as expected.
- Common Causes: Skipping the testing phase after completing the wiring installation.
How to Avoid This:
- Perform continuity tests on all wiring, especially for the fuel system, ignition system, and sensor connections.
- Use an OBD scanner or ECU diagnostic tool to check for faults or error codes related to the wiring system.
- Run a system-wide test before attempting to start the engine, ensuring all components are wired correctly and receiving the necessary power.
Conclusion for Troubleshooting:
Avoiding these common wiring mistakes is crucial to the success of your 2JZ engine swap. By taking the time to properly wire and troubleshoot the system, you’ll ensure that your 2JZ engine runs smoothly and efficiently. A little extra effort in the wiring phase can save you hours of troubleshooting and potentially costly repairs down the road.
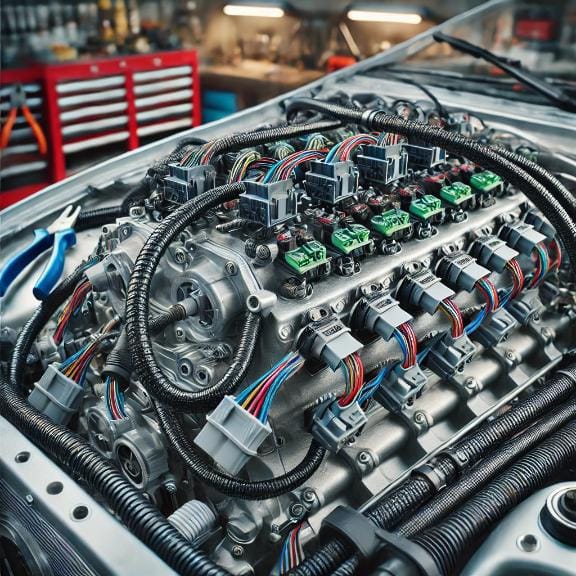

Final Wiring Checks and Testing
After spending hours wiring your 2JZ engine swap, it’s crucial to perform a thorough final wiring check and conduct testing to ensure that everything is functioning properly. Even the smallest wiring error can prevent the engine from starting or running efficiently. This section will guide you through the essential final checks and testing procedures to make sure your 2JZ swap is ready to fire up.
1. Conduct Continuity and Voltage Checks
Before powering up the engine, it’s essential to test all the wiring for continuity and proper voltage. This step helps identify any potential issues with the wiring, such as disconnected wires, faulty connections, or areas with too much resistance that could lead to electrical problems later.
- Continuity Testing:
- Use a multimeter to check for continuity in all the wires that connect to sensors, the ECU, the fuel system, and the ignition system.
- Start by checking the wires from the ECU to the sensors (crankshaft position, camshaft position, O2 sensors, etc.), ensuring that there are no breaks in the wires.
- Test the fuel injector wiring, fuel pump wiring, and ignition system wiring to make sure they are properly connected.
- If continuity is not present, it means there is a break or disconnection in the wiring that needs to be fixed before continuing.
- Voltage Testing:
- Use your multimeter to check the voltage at key components like the fuel pump, ignition coils, and injectors.
- Ensure that the ECU is providing proper voltage to each system and that all sensors are receiving the appropriate voltage.
- If any voltage readings are off, check the wiring connections and troubleshoot the power sources.
2. Verify Sensor Connections
Next, ensure that all sensors are properly connected and that the wiring is secure. Faulty sensor wiring can lead to inaccurate readings, which can affect fuel delivery, ignition timing, and engine performance.
- Crankshaft and Camshaft Sensors: Ensure that both sensors are wired properly and positioned to give accurate readings. A common issue is misplacing the crankshaft position sensor, which can result in timing issues and engine failure to start.
- Oxygen Sensors: Verify that the O2 sensors are correctly wired and that the connectors are securely fastened to avoid faulty readings that can cause running rich or lean conditions.
- Other Sensors: Double-check the TPS (Throttle Position Sensor), coolant temperature sensor, and knock sensors to make sure they are wired correctly and securely.
3. Test the Fuel and Ignition Systems
Now that the wiring for the fuel system and ignition system is connected, you’ll want to test both systems to ensure they are functioning correctly.
- Fuel System Test:
- Turn the key to the ON position (without starting the engine) and listen for the fuel pump to prime.
- Check that the fuel injectors are firing correctly and that there is no leakage from the fuel lines.
- Use an OBD scanner or diagnostic tool to check for any fuel system-related error codes that might indicate wiring issues or malfunctioning components.
- Ignition System Test:
- With the ignition coils and spark plugs connected, check to ensure that each coil pack is firing at the correct time. This can be done by using a spark tester or observing a visible spark from each coil.
- Verify the connection of the crankshaft position sensor and the camshaft position sensor, as these are critical for ignition timing. Without the correct sensor readings, the ignition system may not fire properly.
- Ensure that all ignition components are securely wired and that there are no loose connections that could cause intermittent sparking.
4. ECU Diagnostic and Error Code Check
Once the wiring checks are complete, it’s time to verify that the ECU is correctly communicating with the engine components and that no errors are present.
- Run an OBD-II Scan:
- Use an OBD-II scanner to check for any error codes related to the wiring or the components connected to the ECU.
- Common error codes to watch for include issues with sensor wiring, fuel system wiring, and ignition timing. These errors may point to poor connections or incorrect wiring.
- Clear Error Codes:
- Once any error codes have been addressed, use the scanner to clear the codes and perform another test to ensure that everything is functioning as expected.
5. Double-Check Grounding
Proper grounding is vital for a reliable and efficient electrical system. Improper ground connections can lead to voltage drops, electrical noise, and malfunctions.
- Verify Engine Grounding: Check that the engine block is properly grounded to the car’s chassis. This ensures that the ECU, sensors, and fuel system all receive a stable electrical signal.
- Check ECU Grounds: The ECU typically requires a ground wire for proper signal processing. Verify that the ECU is securely grounded to the vehicle’s chassis or engine block to avoid signal loss or interference.
6. Final Visual Inspection
After conducting all the checks and tests, perform a final visual inspection of all the wiring and connections in the engine bay. Look for any signs of wear, loose connectors, or exposed wires that could lead to issues once the engine is running.
- Ensure that all wires are securely fastened and routed neatly.
- Make sure that no wires are touching heat sources or moving parts.
- Inspect all fuses and relays to ensure they are properly connected and functional.
Conclusion for Testing and Checks:
Once you’ve completed all of the final wiring checks and testing, you can proceed with confidence knowing that the electrical system for your 2JZ swap is correctly set up. These final steps are crucial to ensure the 2JZ engine runs smoothly and avoids electrical issues that could lead to costly repairs down the road. Always take the time to properly test your system and address any issues before starting the engine.
Conclusion: Successfully Wiring Your 2JZ Engine Swap
Congratulations! You’ve successfully navigated the complex process of wiring a 2JZ engine swap into your vehicle. Whether you’ve used the stock ECU, opted for a standalone ECU, or modified the wiring harness, completing the electrical setup is one of the most critical and rewarding steps in this engine swap journey.
Key Takeaways
- Careful Planning is Essential: Before diving into the wiring process, it’s crucial to understand the components that need to be wired, such as the ECU, fuel system, ignition system, and sensors. Planning ahead ensures that each wire is connected correctly and avoids costly mistakes.
- Choose the Right ECU for Your Build: Whether you go with a stock ECU, standalone ECU, or plug-and-play option, make sure that the ECU you choose can support the modifications you plan to make and that it will integrate seamlessly with your vehicle’s wiring system.
- Modifying the Wiring Harness: Depending on the type of swap and your vehicle’s configuration, you may need to modify or build a custom wiring harness. This process involves integrating the 2JZ engine with your car’s existing electrical systems, ensuring that all connectors are in the right places and that the wiring is secure and free from interference.
- Testing Is Key: Always conduct thorough continuity tests and voltage checks before firing up your engine. Properly test the fuel system, ignition system, and ECU connections to ensure there are no wiring errors that could cause misfires or electrical issues.
- Avoid Common Wiring Mistakes: As with any complex project, it’s easy to make mistakes, but taking extra care to check pinouts, connections, and grounding will save you time and frustration. Make sure to route wires away from heat sources and moving parts, and double-check your work with a multimeter or OBD scanner.
- Enjoy the Fruits of Your Labor: Once all the electrical systems are connected, tested, and working properly, it’s time to fire up your 2JZ-powered vehicle. With your hard work and attention to detail, you can expect a smooth-running engine and a successful swap.
Final Thoughts
Wiring a 2JZ engine swap might seem intimidating at first, but with the right knowledge and tools, it’s an entirely manageable process. The key is to take your time, use quality components, and test thoroughly before turning the engine over for the first time. A successful electrical setup ensures that your 2JZ engine runs reliably, efficiently, and with the performance you’ve dreamed of.
Good luck with your 2JZ engine swap, and enjoy the power, precision, and performance that comes with one of Toyota’s most iconic engines.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How do I wire a 2JZ engine swap?
Wiring a 2JZ engine swap involves several key steps, including selecting the right ECU (stock, standalone, or plug-and-play), modifying or building a wiring harness, and connecting various sensors, injectors, and components. Start by planning out the wiring for the fuel system, ignition system, and sensor wiring. Make sure to follow the 2JZ wiring diagram specific to your vehicle and engine variant. After wiring the components, perform continuity tests and voltage checks to ensure everything is functioning correctly before starting the engine.
Can I use a stock ECU for a 2JZ engine swap?
Yes, it is possible to use the stock ECU for a 2JZ engine swap, especially if you’re using an OEM engine (like the 2JZ-GTE from a Toyota Supra) and plan to keep things close to factory spec. However, the stock ECU may limit your ability to make significant modifications or tune the engine for performance. In many cases, a standalone ECU is recommended, especially for high-performance builds or when using upgraded components like larger turbos or injectors. If you choose the stock ECU, modifications to the wiring harness may be necessary.
What are the most common wiring mistakes when swapping a 2JZ engine?
The most common wiring mistakes in a 2JZ engine swap include:
- Incorrect pinouts and miswired connectors: Ensuring the correct pins are used for each sensor and ECU is essential.
- Poor grounding: Insufficient or improper ground connections can lead to electrical issues, misfires, or engine malfunctions.
- Using the wrong wire gauge for high-current components like fuel pumps and ignition systems.
- Overlooking protective measures for wiring near heat sources or moving parts.
- Not verifying sensor wiring: Incorrectly wiring crankshaft, camshaft, or O2 sensors can prevent the engine from running or cause performance issues.
How do I wire a 2JZ fuel system for an engine swap?
Wiring the fuel system in a 2JZ swap involves connecting the fuel injectors, fuel pump, and fuel pressure regulator to the appropriate components in the vehicle’s electrical system. Each fuel injector is typically wired with a signal wire from the ECU and a ground wire. The fuel pump should be wired to a power source and relay to ensure it primes and operates correctly when the ignition is on. The fuel pressure regulator should be connected to the fuel rail and have both power and ground connections. Ensure that all wires are properly shielded from heat and moving parts to avoid damage.
How do I test the wiring after completing a 2JZ swap?
After completing the wiring for your 2JZ engine swap, it’s important to perform several tests to ensure everything works as it should:
- Continuity Test: Use a multimeter to check for continuity in the wiring. This ensures there are no breaks or faulty connections in critical wires, such as the fuel injectors, sensors, and ECU.
- Voltage Test: Verify that each component (fuel pump, ignition coils, sensors) is receiving the proper voltage. Ensure that the ECU is providing correct voltage signals to the fuel injectors and other components.
- Sensor Function Test: Check that the crankshaft position sensor, camshaft position sensor, and O2 sensors are correctly wired and communicating with the ECU.
- Ignition System Test: Ensure that each ignition coil is firing correctly and that the spark plugs are receiving proper signals from the ECU.
- OBD Scan: Run a diagnostic scan to check for any error codes or issues that may indicate wiring problems.