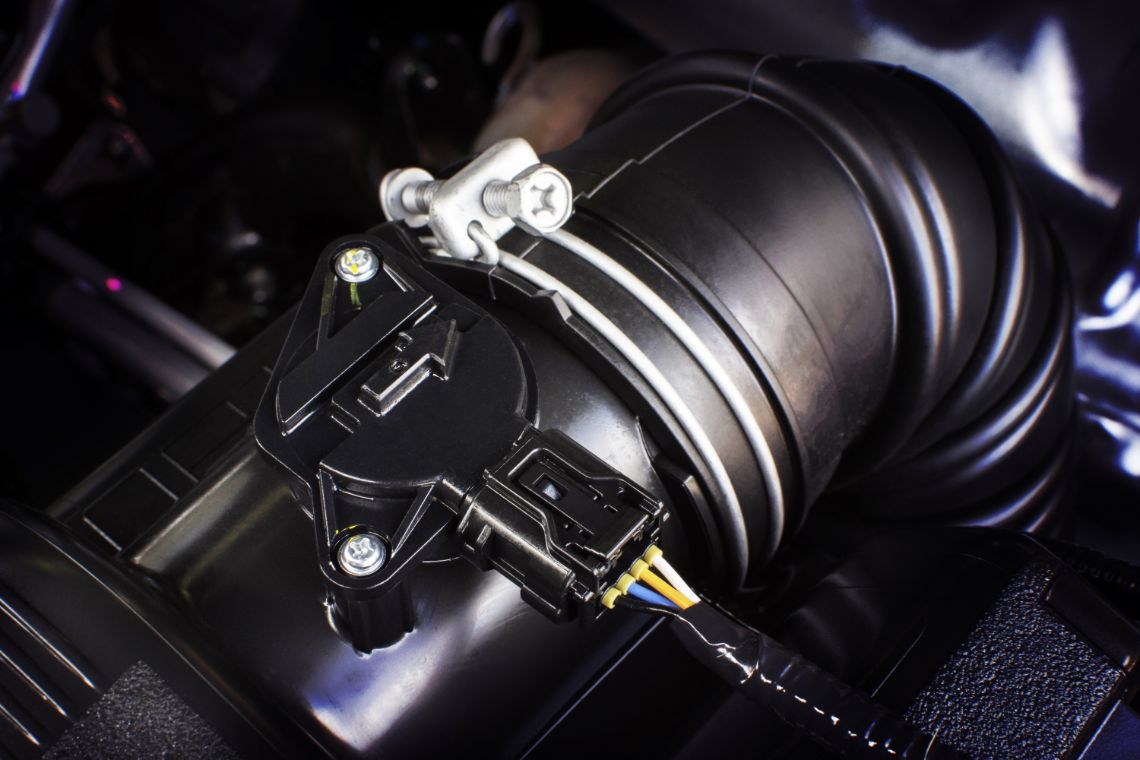
The Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor is a critical component in your vehicle’s engine management system. Its primary function is to measure the amount of air entering the engine, which is crucial for maintaining the optimal air-fuel ratio required for efficient combustion. For car enthusiasts, especially those with performance engines like the 2JZ-GTE, understanding the importance of the MAF sensor and how to address its malfunctions is key to maintaining peak engine performance.
Why the MAF Sensor Matters
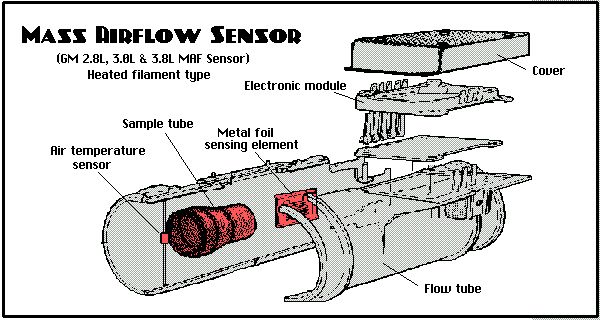
The MAF sensor plays a vital role in ensuring that the engine receives the correct amount of air for the combustion process. It sends data to the engine control unit (ECU), which then adjusts the fuel injection accordingly. Any malfunction in the MAF sensor or its circuit can lead to a range of issues, from reduced fuel efficiency to significant engine performance problems. This is why it’s essential to recognize the symptoms of MAF sensor issues and know how to address them effectively.
Introduction to MAF Circuit Malfunctions
Mass Air Flow circuit malfunctions can stem from various causes, including sensor contamination, wiring issues, and complete sensor failure. These malfunctions can manifest through symptoms like rough idling, poor acceleration, and the illumination of the check engine light. Understanding these symptoms and their underlying causes allows car enthusiasts to diagnose and fix problems promptly, ensuring their engines run smoothly.
Importance of Addressing MAF Circuit Malfunctions
Ignoring MAF circuit malfunctions can lead to more severe engine issues and costly repairs. By identifying and addressing these problems early, you can prevent further damage and maintain the optimal performance of your engine. This guide will provide an in-depth look at common MAF circuit malfunctions, how to diagnose them, and the best practices for maintaining your MAF sensor and circuit.
In this comprehensive article, we will cover:
- An overview of the Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor and its function.
- Common MAF circuit malfunctions, their causes, and symptoms.
- Diagnostic tools and techniques for identifying MAF sensor issues.
- Best practices for maintaining the MAF sensor and circuit to prevent future malfunctions.
By the end of this guide, you will be equipped with the knowledge to effectively diagnose and resolve MAF circuit malfunctions, ensuring your engine continues to perform at its best.
Overview of the Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor
The Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor is a key component in the engine management system of modern vehicles. Its primary function is to measure the amount of air entering the engine, which is crucial for maintaining the optimal air-fuel ratio required for efficient combustion.
Function and Importance of the MAF Sensor
The MAF sensor measures the volume and density of air entering the engine’s intake manifold. It sends this information to the engine control unit (ECU), which uses it to calculate the correct amount of fuel to inject into the combustion chamber. This ensures that the engine operates efficiently, providing optimal performance and fuel economy.
How the MAF Sensor Works
The MAF sensor typically works using either a hot wire or a vane meter:
- Hot Wire MAF Sensor: This type uses an electrically heated wire. As air flows past the wire, it cools down, and the sensor measures the change in electrical resistance. The ECU uses this data to determine the air mass entering the engine.
- Vane Meter MAF Sensor: This type uses a spring-loaded vane that moves in response to incoming air. The position of the vane is measured and converted into an electrical signal that the ECU interprets to calculate the air mass.
Common Signs of MAF Sensor Issues
When the MAF sensor or its circuit malfunctions, it can lead to various engine performance issues. Common symptoms include:
- Rough Idling: The engine may idle roughly or stall.
- Poor Acceleration: There may be a noticeable lack of power during acceleration.
- Check Engine Light: The check engine light may illuminate on the dashboard.
- Increased Fuel Consumption: The engine may consume more fuel than usual.
- Black Smoke from the Exhaust: Excessively rich air-fuel mixture may cause black smoke.
Understanding these symptoms and their implications can help in diagnosing and addressing MAF sensor issues promptly.
Common Mass Air Flow Circuit Malfunctions
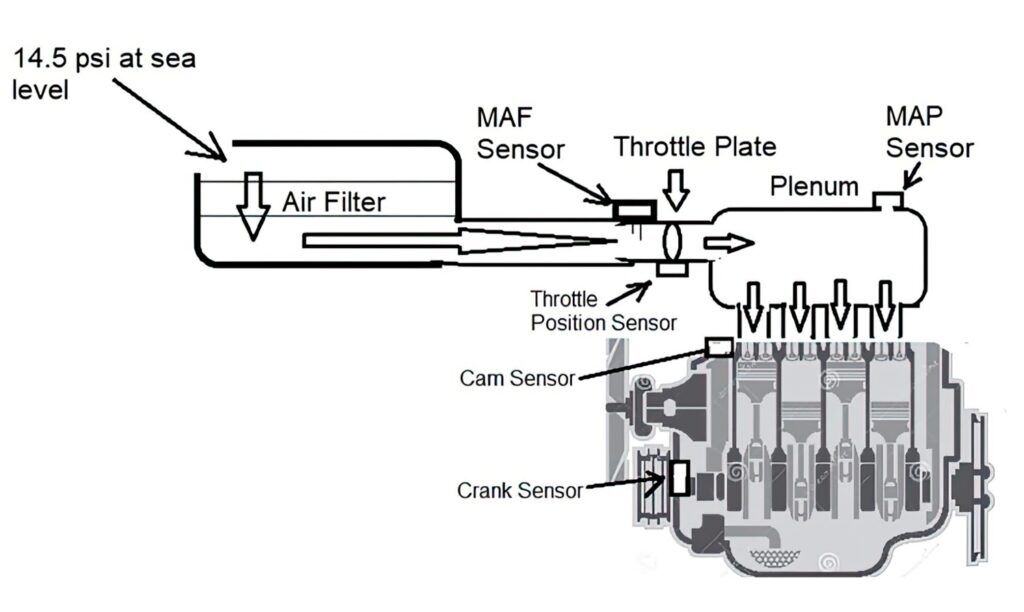
Mass Air Flow circuit malfunctions can stem from various causes, each with its unique symptoms and diagnostic challenges. Here are some of the most common malfunctions:
Malfunction 1: Sensor Contamination
- Description and Causes: Over time, the MAF sensor can become contaminated with dirt, oil, and other debris. This contamination affects the sensor’s ability to accurately measure the airflow.
- Symptoms and Effects on Engine Performance: Contaminated sensors may cause rough idling, poor acceleration, and increased fuel consumption.
- Diagnostic Procedures: Inspect the MAF sensor for visible dirt and debris. Use an OBD II scanner to check for codes like P0101 (MAF Sensor Performance).
- Solutions and Preventive Measures: Clean the MAF sensor using a specialized MAF sensor cleaner. Avoid using oil-based air filters that can contribute to contamination.
Malfunction 2: Wiring Issues
- Description and Causes: The MAF sensor relies on a network of wires to transmit data to the ECU. Damaged or frayed wires can disrupt this communication.
- Symptoms and Effects on Engine Performance: Wiring issues may cause intermittent engine performance problems, rough idling, and the check engine light to come on.
- Diagnostic Procedures: Visually inspect the wiring for damage. Use a multimeter to test for continuity and proper voltage.
- Solutions and Preventive Measures: Repair or replace damaged wires. Ensure that the wiring harness is properly secured and protected from heat and abrasion.
Malfunction 3: Sensor Failure
- Description and Causes: The MAF sensor itself can fail due to age, manufacturing defects, or exposure to harsh conditions.
- Symptoms and Effects on Engine Performance: A failed MAF sensor may cause the engine to run rich or lean, resulting in poor performance and increased emissions.
- Diagnostic Procedures: Use an OBD II scanner to check for codes like P0102 (MAF Circuit Low Input) or P0103 (MAF Circuit High Input). Perform voltage and resistance tests on the sensor.
- Solutions and Preventive Measures: Replace the faulty MAF sensor. Ensure that the new sensor is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model.
Diagnostic Tools and Techniques
To effectively diagnose and resolve MAF sensor issues, having the right tools and knowledge is essential. Here are the key diagnostic tools and techniques you’ll need:
Essential Diagnostic Tools for MAF Sensor Issues
- OBD II Scanner: A crucial tool for reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and real-time engine data.
- Multimeter: Useful for testing electrical components and circuits.
- MAF Sensor Cleaner: Specialized cleaner for removing contamination from the sensor without damaging it.
- Inspection Mirror and Flashlight: For visually inspecting hard-to-reach areas.
How to Use an OBD II Scanner to Diagnose MAF Circuit Malfunctions
- Connecting the OBD II Scanner: Locate the OBD II port under the dashboard, connect the scanner, and turn on the ignition. Follow the scanner’s instructions to retrieve DTCs and view real-time data.
- Interpreting DTCs: Look for codes related to the MAF sensor, such as P0100 (MAF Circuit Malfunction), P0101 (MAF Sensor Performance), P0102 (MAF Circuit Low Input), and P0103 (MAF Circuit High Input).
- Real-Time Data Monitoring: Use the scanner to monitor real-time data from the MAF sensor. Compare the readings to the manufacturer’s specifications.
Step-by-Step Guide to Testing and Diagnosing MAF Sensor Issues
- Preliminary Inspection: Perform a visual inspection of the MAF sensor and its wiring. Look for visible damage or contamination.
- Voltage Testing: Use a multimeter to check the voltage at the MAF sensor’s connector. Compare the readings to the specifications in your vehicle’s service manual.
- Resistance Testing: Test the resistance of the MAF sensor’s internal circuitry using a multimeter. Ensure the readings are within the specified range.
- Cleaning the Sensor: If the sensor is contaminated, clean it with MAF sensor cleaner. Allow it to dry completely before reinstalling.
Case Studies and Examples
- Case Study 1: Diagnosing a rough idling issue. The OBD II scanner showed a P0101 code. Upon inspection, the MAF sensor was found to be heavily contaminated. Cleaning the sensor resolved the issue.
- Case Study 2: Addressing poor acceleration. The OBD II scanner indicated a P0102 code. A visual inspection revealed damaged wiring. Repairing the wiring restored normal engine performance.
Best Practices for Maintaining the MAF Sensor and Circuit
To keep the MAF sensor and its circuit in optimal condition, regular maintenance is essential. Here are some best practices to follow:
Regular Maintenance Tips for the MAF Sensor
- Periodic Cleaning: Clean the MAF sensor at regular intervals using a specialized MAF sensor cleaner. This prevents contamination and ensures accurate readings.
- Inspection: Regularly inspect the MAF sensor and its wiring for signs of damage or wear. Address any issues promptly to avoid malfunctions.
Cleaning and Inspecting the MAF Sensor
- Remove the Sensor: Carefully remove the MAF sensor from the intake system.
- Clean the Sensor: Spray the sensor with MAF sensor cleaner. Avoid touching the sensor’s delicate components.
- Reinstall the Sensor: Once the sensor is dry, reinstall it and ensure it is securely fastened.
Preventive Measures to Avoid MAF Circuit Malfunctions
- Avoid Oil-Based Air Filters: Oil from these filters can contaminate the MAF sensor. Use dry air filters instead.
- Secure Wiring: Ensure that the MAF sensor’s wiring harness is properly secured and protected from heat and abrasion.
Scheduling and Record-Keeping
- Maintenance Schedule: Follow a consistent maintenance schedule based on your vehicle’s service manual.
- Record-Keeping: Keep detailed records of all maintenance and repairs. This helps track the sensor’s condition and ensures all necessary tasks are completed.
By following these best practices, you can keep your MAF sensor and its circuit in top condition, ensuring reliable engine performance and longevity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, addressing Mass Air Flow circuit malfunctions is essential for maintaining the optimal performance and longevity of your engine. The MAF sensor plays a critical role in ensuring the engine receives the correct air-fuel mixture, which is crucial for efficient combustion and overall engine health. By understanding the common symptoms of MAF sensor issues, using the appropriate diagnostic tools, and following best practices for maintenance, car enthusiasts can prevent major engine problems and ensure their vehicles run smoothly.
Neglecting MAF sensor issues can lead to poor engine performance, increased fuel consumption, and even costly repairs. Therefore, it is vital to regularly inspect, clean, and maintain the MAF sensor and its circuit. Implementing preventive measures, such as avoiding oil-based air filters and securing the wiring harness, can further help in preventing MAF circuit malfunctions.
If you own a vehicle equipped with a MAF sensor, make it a habit to include regular MAF sensor inspections and maintenance in your routine. Invest in a quality OBD II scanner and learn to interpret the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) related to the MAF sensor. By staying proactive, you can ensure your engine delivers the performance and reliability it was designed for.
Start today by performing a thorough inspection of your MAF sensor and its circuit. Use the steps outlined in this guide to diagnose and address any issues you find. With regular maintenance and timely interventions, you can keep your engine in peak condition and enjoy a better driving experience.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the function of the Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor?
The MAF sensor measures the volume and density of air entering the engine’s intake manifold. This information is sent to the engine control unit (ECU), which uses it to calculate the correct amount of fuel to inject for efficient combustion.
How can I tell if my MAF sensor is malfunctioning?
Common symptoms of a malfunctioning MAF sensor include rough idling, poor acceleration, increased fuel consumption, the check engine light coming on, and black smoke from the exhaust. Using an OBD II scanner to check for related DTCs can help confirm the issue.
What are the common causes of MAF circuit malfunctions?
Common causes include sensor contamination, wiring issues, and sensor failure. Contamination can occur due to dirt and debris, while wiring issues can result from frayed or damaged wires. Sensor failure can be due to age, manufacturing defects, or exposure to harsh conditions.
How can I diagnose a MAF sensor issue?
Use an OBD II scanner to retrieve DTCs related to the MAF sensor. Perform a visual inspection of the sensor and its wiring. Use a multimeter to test the voltage and resistance of the sensor. Clean the sensor if it appears contaminated.
What are the best practices for maintaining the MAF sensor and circuit?
Regularly clean the MAF sensor using a specialized cleaner, inspect the sensor and its wiring for damage, avoid using oil-based air filters, and ensure the wiring harness is properly secured and protected. Following a consistent maintenance schedule and keeping detailed records of all maintenance activities are also essential.
By incorporating these best practices into your maintenance routine, you can ensure your MAF sensor and its circuit remain in optimal condition, contributing to the overall performance and longevity of your engine.
