Ignition coils are critical components in the 2JZ-GTE engine, responsible for converting the battery’s low voltage into the high voltage needed to create a spark at the spark plugs. When ignition coils malfunction, they can cause a range of engine performance issues, including misfires, rough idling, and decreased fuel efficiency. In this article, we will explore the importance of ignition coils, common issues that can arise, and provide a detailed guide on diagnosing and repairing ignition coil issues to ensure your 2JZ-GTE engine runs smoothly.
Understanding Ignition Coils
Components and Functions:
The ignition coil in the 2JZ-GTE engine consists of several key components:
- Primary Coil: Receives low voltage from the battery and generates a magnetic field.
- Secondary Coil: Converts the magnetic field into a high voltage current.
- Spark Plug Connector: Transmits the high voltage current to the spark plug to ignite the air-fuel mixture.
These components work together to ensure the engine receives a strong and consistent spark for optimal combustion.
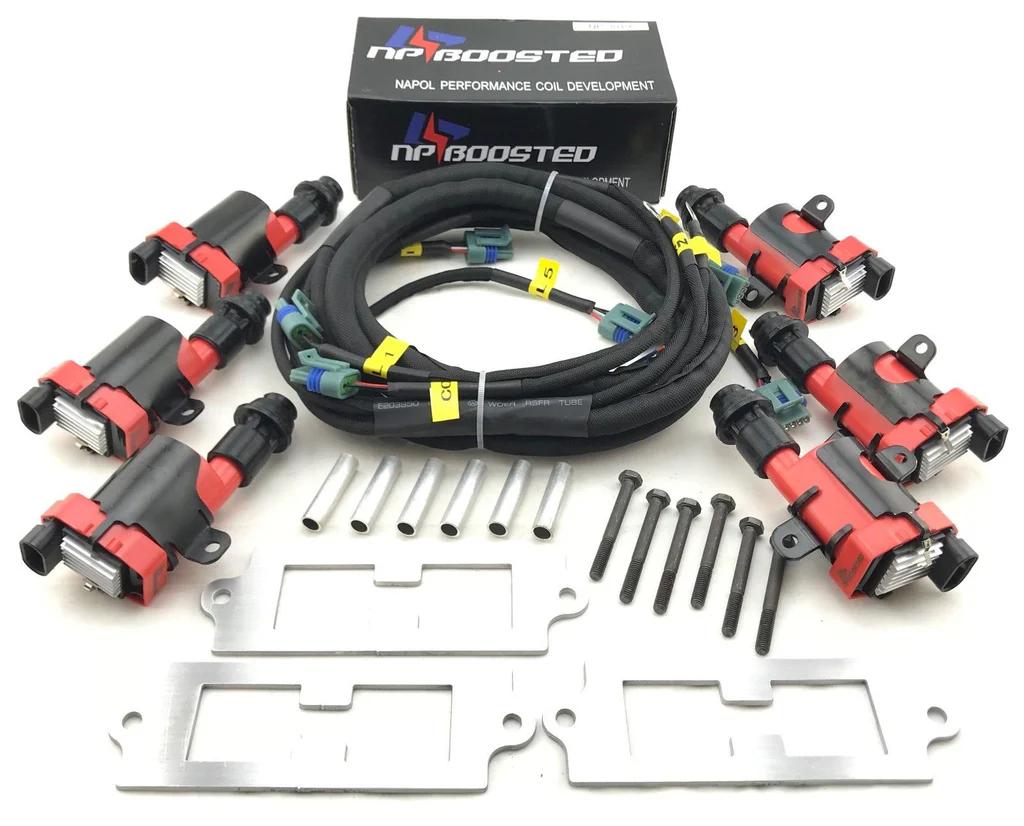

Common Issues with Ignition Coils:
Several common issues can affect ignition coils:
- Coil Failure: Worn or damaged coils can fail to produce the necessary voltage.
- Electrical Problems: Issues with the wiring or connectors can disrupt the signal to the ignition coils.
- Heat Damage: Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can degrade the coil’s insulation and components.
- Moisture Damage: Water or moisture intrusion can short-circuit the ignition coil.
Diagnosing Ignition Coil Issues
Step-by-Step Diagnostic Procedures:
- Using an OBD II Scanner:
- Connect the Scanner: Plug the OBD II scanner into the vehicle’s diagnostic port.
- Read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Check for any stored DTCs related to the ignition system. Common codes include P0300 (Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected), P0351 (Ignition Coil A Primary/Secondary Circuit Malfunction), and P0352 (Ignition Coil B Primary/Secondary Circuit Malfunction).
- Live Data Monitoring: Use the scanner to monitor real-time data such as engine RPM and misfire counts. Compare these values to the manufacturer’s specifications to identify any discrepancies.
- Visual Inspection:
- Wiring and Connectors: Inspect the wiring and connectors related to the ignition coils for signs of wear, damage, or corrosion.
- Ignition Coils: Check the ignition coils for physical damage, such as cracks or burn marks.
- Spark Test:
- Procedure: Use a spark tester to check if each ignition coil is producing a strong and consistent spark. Disconnect the spark plug wire from the spark plug, connect the spark tester, and crank the engine. Observe the spark and compare it to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Resistance Testing:
- Primary Coil: Use a multimeter to measure the resistance of the primary coil. Place the multimeter probes on the primary terminals of the ignition coil and compare the reading to the specified range.
- Secondary Coil: Measure the resistance of the secondary coil by placing the multimeter probes on the secondary terminals. Compare the reading to the specified range.
Repairing Ignition Coil Issues
Mechanical Repairs:
- Ignition Coil Replacement:
- Removal: Disconnect the battery, remove the electrical connectors and bolts securing the faulty ignition coil, and remove it from the engine.
- Installation: Install the new ignition coil, reconnect the electrical connectors, and secure it with the bolts. Reconnect the battery.
- Wiring and Connector Repairs:
- Inspection: Check all wiring and connectors related to the ignition coils for damage or corrosion.
- Repair: Repair or replace damaged wiring and connectors as needed.
Preventive Measures:
- Heat Protection:
- Procedure: Install heat shields or relocate the ignition coils away from high-temperature areas to prevent heat damage.
- Moisture Protection:
- Procedure: Ensure that the ignition coils and connectors are properly sealed to prevent moisture intrusion. Use dielectric grease on the connectors to protect against corrosion.
Preventive Maintenance Tips
Regular maintenance can help prevent many common ignition coil issues:
- Routine Inspections: Inspect the ignition coils, wiring, and connectors regularly for signs of wear or damage.
- Spark Plug Maintenance: Replace spark plugs at regular intervals to prevent excessive load on the ignition coils.
- Heat Management: Ensure proper heat management around the ignition coils to prevent heat damage.
- Moisture Control: Keep the engine compartment dry and ensure proper sealing of ignition coil connectors.
Conclusion
Maintaining the ignition coils is crucial for the optimal performance of your 2JZ-GTE engine. By understanding the components and functions of the ignition coils, recognizing common issues, and following systematic diagnostic and repair procedures, you can ensure your engine runs smoothly and efficiently. Regular preventive maintenance is key to avoiding ignition coil problems and prolonging the life of your engine.
Monitor your engine’s ignition system regularly and take action if you notice any signs of malfunction. Use the diagnostic and repair techniques outlined in this article to address issues promptly. For complex problems or if you are unsure about the repairs, seek professional help to ensure your engine remains in optimal condition.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What causes ignition coil issues in a 2JZ-GTE engine?
Common causes include coil failure, electrical problems, heat damage, and moisture damage.
How can I diagnose ignition coil issues in my 2JZ-GTE engine?
Use an OBD II scanner to read diagnostic trouble codes and monitor live data. Perform visual inspections, spark tests, and resistance testing.
What are the symptoms of ignition coil issues?
Symptoms include engine misfires, rough idling, decreased fuel efficiency, and check engine light activation.
Can ignition coil issues damage my engine?
Yes, if left unaddressed, ignition coil issues can lead to poor performance, increased emissions, and potential engine damage.
How can I prevent ignition coil issues?
Preventive measures include routine inspections, spark plug maintenance, heat management, and moisture control.