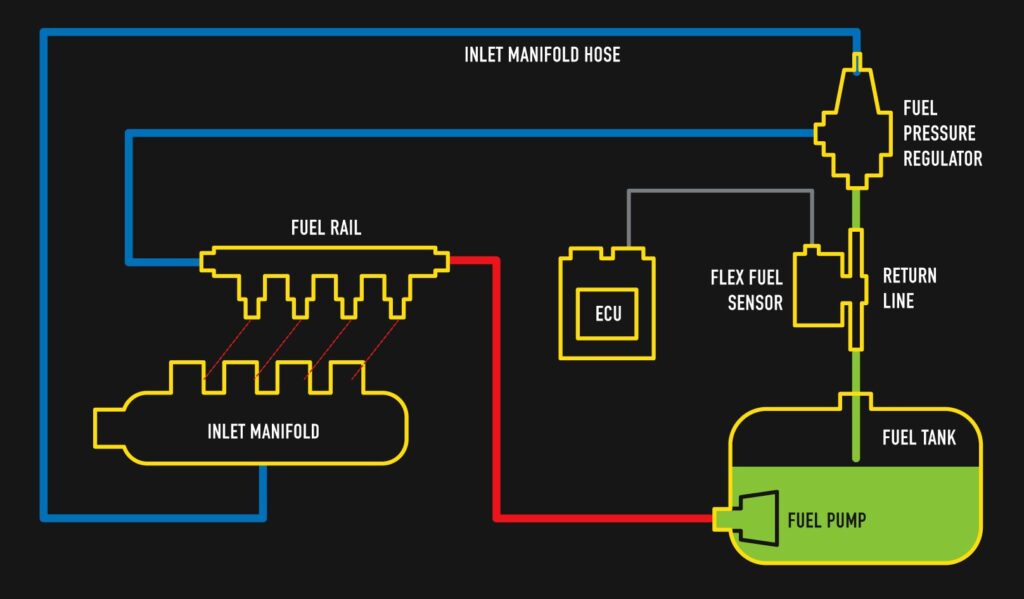
The 2JZ-GTE engine, renowned for its power and reliability, is a favorite among car enthusiasts. Central to its performance is the fuel pump control circuit, which ensures that the engine receives a steady supply of fuel. A properly functioning fuel pump control circuit is crucial for maintaining optimal engine performance and efficiency.
In this article, we will explore the significance of the fuel pump control circuit, common issues that may arise, and detailed diagnostic and troubleshooting procedures. By understanding and maintaining this critical component, you can ensure that your 2JZ-GTE engine runs smoothly and efficiently.
Understanding the Fuel Pump Control Circuit
Function: The fuel pump control circuit is responsible for delivering fuel from the fuel tank to the engine. The circuit includes components such as the fuel pump relay, wiring, and the Engine Control Module (ECM). The ECM controls the fuel pump relay, which in turn activates the fuel pump to provide the necessary fuel pressure for the engine to operate efficiently.
Components:
- Fuel Pump Relay: Acts as a switch to control the power supply to the fuel pump.
- Wiring: Connects the various components of the fuel pump control circuit.
- Engine Control Module (ECM): Monitors and controls the fuel pump relay and other engine functions.
Importance: A properly functioning fuel pump control circuit ensures that the engine receives the right amount of fuel under all operating conditions. Any issues with this circuit can lead to engine performance problems, such as poor acceleration, stalling, or failure to start.
Common Issues with the Fuel Pump Control Circuit
Faulty Fuel Pump Relay:
- Symptoms: The engine may not start, or there could be intermittent power loss to the fuel pump.
- Causes: Relay contacts may become worn or corroded, or the relay itself may fail.
- Solutions: Check the fuel pump relay for signs of wear or corrosion. Replace the relay if necessary.
Wiring Problems:
- Symptoms: Intermittent power loss, erratic engine behavior, or failure to start.
- Causes: Damaged or corroded wires, loose connections, or short circuits.
- Solutions: Inspect the wiring for any signs of damage or corrosion. Repair or replace damaged wires and secure any loose connections.
ECM Issues:
- Symptoms: The fuel pump may not receive the proper signals to operate.
- Causes: Faulty ECM or issues with the ECM’s software.
- Solutions: Check the ECM for any error codes. If the ECM is faulty, it may need to be reprogrammed or replaced.
Connector Problems:
- Symptoms: Similar to wiring problems, with intermittent power loss or failure to start.
- Causes: Dirty or corroded connectors, loose connections.
- Solutions: Clean the connectors and ensure they are securely connected. Replace any damaged connectors.
Diagnostic Procedures for the Fuel Pump Control Circuit
Using a Multimeter:
- Voltage Check: Use a multimeter to check the voltage at various points in the fuel pump control circuit. Ensure that the voltage readings are within the specified range.
- Continuity Test: Check the continuity of the wires and connectors in the fuel pump control circuit to ensure there are no breaks or short circuits.
Step-by-Step Diagnostic Procedures:
- Fuel Pump Relay Inspection:
- Visual Check: Inspect the fuel pump relay for any signs of wear or corrosion.
- Relay Testing: Use a multimeter to test the relay’s resistance and functionality. Replace the relay if it fails the test.
- Wiring Inspection:
- Visual Check: Inspect the wiring for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Continuity Test: Use a multimeter to check the continuity of the wires. Repair or replace any components that do not have continuity.
- ECM Inspection:
- Error Code Check: Use an OBD II scanner to check the ECM for any error codes related to the fuel pump control circuit.
- Voltage Check: Measure the voltage at the ECM power and signal terminals to ensure they are within the specified range.
- ECM Replacement: If the ECM is faulty, it may need to be reprogrammed or replaced.
- Connector Inspection:
- Visual Check: Inspect the connectors for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Continuity Test: Use a multimeter to check the continuity of the connectors. Clean or replace any damaged connectors.
Preventive Maintenance Tips
Regular Relay Checks: Regularly check the fuel pump relay’s condition to ensure it is functioning correctly. Replace the relay if it shows signs of wear or corrosion.
Wiring Inspections: Inspect the wiring for any signs of damage or corrosion during routine maintenance. Repair or replace any damaged wires to prevent power loss issues.
Connector Maintenance: Ensure all connectors are clean and securely connected. Regularly inspect connectors for any signs of damage or corrosion and replace them if necessary.
Conclusion
Maintaining the fuel pump control circuit is essential for the optimal performance of the 2JZ-GTE engine. By understanding the circuit’s components, recognizing common issues, and following proper diagnostic and maintenance procedures, you can ensure that your engine runs smoothly.
Regularly inspect and maintain the fuel pump control circuit to avoid performance issues. If you experience any symptoms of a faulty circuit, follow the diagnostic procedures outlined in this article. For more complex issues, seek professional help to ensure your engine remains in top condition.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the fuel pump control circuit?
The fuel pump control circuit supplies the necessary electrical power to the fuel pump, ensuring that the engine receives a steady supply of fuel.
How do I check the fuel pump control circuit in my 2JZ-GTE engine?
Use a multimeter to check the voltage and continuity of the fuel pump relay, wiring, ECM, and connectors in the fuel pump control circuit.
Can I drive with a faulty fuel pump control circuit?
It is not recommended to drive with a faulty fuel pump control circuit, as it can lead to engine performance issues and potential failure.
What tools do I need to diagnose the fuel pump control circuit?
A multimeter and an OBD II scanner are essential tools for diagnosing the fuel pump control circuit. They allow you to measure voltage, continuity, and check for error codes.
How often should I check the fuel pump control circuit?
Regularly check the fuel pump control circuit during routine maintenance or if you notice any changes in engine performance or behavior.