The Toyota 2JZ engine is a marvel of engineering that has earned legendary status among automotive enthusiasts worldwide. Known for its durability, versatility, and immense power potential, this inline-six engine has become a cornerstone of high-performance builds. From its robust stock capabilities to its ability to handle extreme modifications, the 2JZ is the go-to choice for those looking to extract the utmost performance from their vehicle.
In this article, we delve into the key factors that influence the power output of the 2JZ engine. These include the role of fuel quality, boost pressure, turbo upgrades, and engine management systems in achieving peak performance. Whether you’re a seasoned tuner or new to the world of engine modifications, this comprehensive guide will equip you with the insights needed to unlock the true potential of the 2JZ.
Are you ready to embark on this journey of horsepower and performance optimization? 🚗💨
Overview of the 2JZ Engine
Historical Background
The Toyota 2JZ engine was introduced in the early 1990s as part of Toyota’s JZ engine family, designed to offer both reliability and performance. Initially debuted in the Toyota Aristo (marketed as the Lexus GS300 in some regions), the 2JZ-GTE variant gained global fame with its inclusion in the fourth-generation Toyota Supra, also known as the MKIV Supra. This engine quickly became a symbol of Japanese engineering excellence, revered for its ability to handle extreme power levels while maintaining reliability.
Key Specifications
The 2JZ engine is celebrated for its robust design and advanced features:
- Engine Type: Inline-6
- Displacement: 3.0L (2,997 cc)
- Block Material: Cast iron, ensuring exceptional strength and resistance to warping under high stress.
- Head Material: Aluminum alloy, contributing to weight reduction and efficient heat dissipation.
- Valvetrain: Dual Overhead Camshaft (DOHC) with 24 valves, allowing for precise airflow management.
- Forced Induction: Twin sequential turbochargers in the 2JZ-GTE model, offering a balance of low-end torque and high-end power.
Stock Power Capabilities
The 2JZ-GTE, under Japan’s “gentlemen’s agreement,” was rated at 280 horsepower (PS) to comply with domestic power regulations. However, this figure belies the engine’s true potential, as enthusiasts have demonstrated its capability to handle up to 600 horsepower with completely stock internals. This makes the 2JZ a preferred choice for tuners aiming to achieve high performance without extensive modifications.
Fuel System Optimization
Fuel Quality and Octane Ratings
Fuel quality is a critical factor in maximizing the power output of the 2JZ engine. High-performance engines like the 2JZ thrive on high-octane fuels, which resist knocking and detonation under high compression and boost pressures. Using fuel with an octane rating of 95 or higher allows for aggressive tuning and greater ignition timing, unlocking additional power without compromising engine reliability.
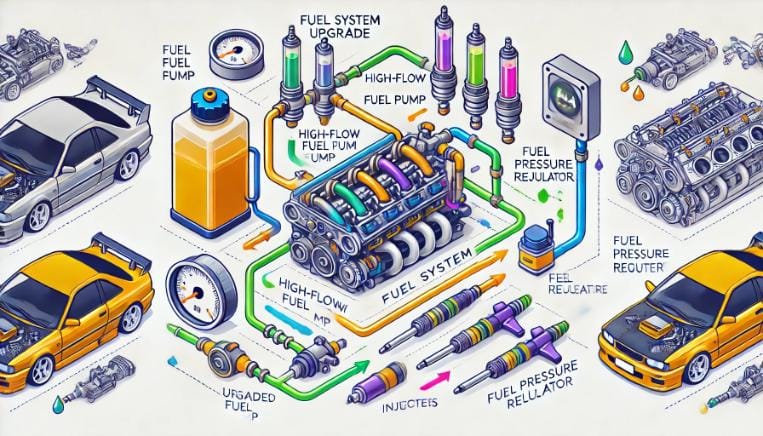
Aftermarket Fuel Components
As power levels increase, the demand for fuel delivery grows. Upgrading the fuel system ensures that the engine receives an adequate and consistent supply of fuel:
- High-Flow Fuel Pumps: Aftermarket options such as the Walbro 255 and AEM 340 LPH pumps support significantly higher horsepower outputs compared to the stock unit.
- Fuel Injectors: High-capacity injectors, ranging from 750cc to 2,000cc, are essential for delivering the fuel needed in forced induction setups.
- Fuel Pressure Regulators: Upgraded regulators ensure stable fuel pressure, critical for maintaining consistent performance during high-demand situations.
Tuning for Fuel Efficiency
Optimizing the air-fuel ratio (AFR) is crucial for balancing power and reliability. With the help of a modern Engine Management System (EMS), tuners can achieve precise control over fuel delivery, ensuring:
- Efficient combustion for power gains.
- Avoidance of lean conditions that could lead to engine damage.
- Enhanced throttle response and drivability.
Forced Induction and Boost Management
Sequential Turbo System
The 2JZ-GTE’s factory twin-turbo setup utilizes a sequential configuration, where one turbo operates at lower RPMs for quick spool and responsiveness, while the second turbo engages at higher RPMs to provide additional boost. This system delivers a seamless balance of low-end torque and high-end power, making it ideal for street and performance applications. However, the stock turbos have limitations, particularly when pushing beyond factory power levels.
Upgrading Turbochargers
As power demands increase, upgrading the turbochargers becomes essential. Two common approaches include:
- Single Turbo Conversion: A larger single turbo, such as a Garrett GTX or Precision Turbo, simplifies the system while providing significant horsepower gains. Although this can lead to increased turbo lag, the overall efficiency and top-end power justify the trade-off for high-performance builds.
- Upgraded Twin Turbo Setup: Retaining a twin-turbo configuration with upgraded turbos, such as HKS GT2835 units, maintains the quick spool characteristic while boosting overall capacity.
Managing Boost Pressure
Boost pressure is a critical component of forced induction performance. Proper management is essential to maximize power while protecting engine components:
- Wastegates: These devices regulate exhaust flow to the turbo, preventing overboost conditions.
- Boost Controllers: Electronic or manual controllers allow for precise adjustment of boost levels to match driving conditions or specific performance needs.
Cooling the Boosted Air
Compressing air increases its temperature, which can reduce efficiency and increase the risk of detonation. Upgrading intercooling systems ensures optimal intake air temperatures:
- Front-Mount Intercoolers (FMIC): Larger, high-efficiency units lower intake air temperatures, improving combustion.
- Water-Methanol Injection: This advanced cooling solution further reduces intake temperatures while increasing the octane effect of the air-fuel mixture.
Engine Management Systems
Stock ECU Capabilities
The stock Engine Control Unit (ECU) in the 2JZ-GTE is a robust system designed to handle factory parameters efficiently. However, its limited flexibility in tuning becomes a bottleneck when power levels exceed stock configurations. While the factory ECU can accommodate modest bolt-on upgrades, it restricts the fine-tuning required for high-performance applications.
Aftermarket ECU Options
Upgrading to a standalone or piggyback ECU is essential for precise control over the engine’s critical parameters, including fuel delivery, ignition timing, and boost pressure. Popular options include:
- AEM Infinity Series: Known for its user-friendly interface and advanced tuning capabilities.
- Haltech Elite Series: Offers extensive customization and support for high-power setups.
- Motec M800: A premium solution for professional-grade tuning and data logging.
These systems allow for real-time adjustments and logging, providing tuners with the tools necessary to optimize performance and reliability.
Importance of Professional Tuning
A professionally tuned ECU ensures that all components work harmoniously, achieving the following:
- Optimized Air-Fuel Ratios: For peak efficiency and power output.
- Knock Prevention: Safeguarding the engine against detonation.
- Improved Throttle Response: Enhancing drivability under varying conditions.
Integration with Supporting Systems
Modern ECUs can integrate seamlessly with additional systems such as:
- Wideband O2 sensors for accurate air-fuel monitoring.
- Boost controllers for dynamic pressure adjustments.
- Data loggers for performance analysis and refinement.
Internal Engine Components
Strength of Stock Internals
One of the 2JZ engine’s most celebrated attributes is the exceptional durability of its stock internal components. With forged pistons, high-strength connecting rods, and a robust crankshaft, the 2JZ-GTE can safely handle up to 600 horsepower with no internal modifications. This strength is a testament to Toyota’s engineering precision, making the engine a favorite among tuners seeking reliable performance.
Upgrading Internals for High Power
When pushing beyond 600 horsepower, upgrading internal components becomes essential to maintain reliability and avoid catastrophic failure. Key upgrades include:
- Forged Pistons: Brands like CP Carrillo and JE Pistons offer lightweight and heat-resistant options, enabling safe operation under extreme boost pressures.
- Connecting Rods: H-beam or I-beam rods provide enhanced durability for high-revving applications.
- Crankshaft: For builds exceeding 1,000 horsepower, a billet crankshaft ensures resistance to torsional stress and fatigue.
- Head Studs: ARP head studs provide improved clamping force, essential for maintaining head gasket integrity under high boost conditions.
Compression Ratio Adjustments
The compression ratio plays a pivotal role in balancing power and reliability:
- Lower Compression Ratios (8.5:1 to 9.0:1): Ideal for high-boost setups, reducing the risk of detonation.
- Stock Compression Ratios (10.0:1): Suitable for moderate forced induction setups, providing a balance between responsiveness and efficiency.
Valvetrain Upgrades
For builds that frequently operate at high RPMs, enhancing the valvetrain is crucial:
- Performance Camshafts: Allow for optimized valve timing, increasing airflow and power output.
- Springs and Retainers: Upgraded components prevent valve float, enabling safe operation at elevated RPMs.
Exhaust System Enhancements
Exhaust Flow Optimization
Efficient exhaust flow is essential for maximizing engine performance. The stock 2JZ exhaust system is designed for balance and emissions compliance but becomes restrictive at higher power levels. Upgrading the exhaust components can significantly improve performance by reducing backpressure and increasing flow efficiency.
Key components for optimization:
- High-Flow Headers: These replace the restrictive factory exhaust manifold, enhancing the evacuation of exhaust gases from the cylinders.
- Downpipes: High-flow or catless downpipes minimize restrictions, improving turbo spool and overall efficiency.
Impact on Turbocharger Efficiency
A well-designed exhaust system complements the turbocharger by:
- Reducing Backpressure: Ensuring that the turbo operates more efficiently and delivers consistent power across the RPM range.
- Improving Spool Times: Allowing the turbo to achieve peak boost more quickly, enhancing responsiveness.
Cat-Back and Straight-Pipe Options
The choice of exhaust configuration depends on the balance between performance and compliance:
- Cat-Back Exhausts: These systems replace the exhaust from the catalytic converter to the rear, offering improved flow while maintaining emissions compliance.
- Straight-Pipe Exhausts: Ideal for track-only vehicles, these systems eliminate restrictions entirely, providing maximum power gains but increasing noise levels significantly.
Exhaust Diameter Considerations
The diameter of the exhaust system impacts airflow:
- 3-Inch Systems: Suitable for moderate power levels, balancing flow and noise.
- 4-Inch Systems: Necessary for extreme power builds, providing unrestricted exhaust flow for high-boost applications.
Material Choices
Choosing the right material for the exhaust system affects durability and weight:
- Stainless Steel: Resistant to corrosion and ideal for high-performance applications.
- Titanium: Lightweight and heat-resistant, offering premium performance at a higher cost.
Cooling and Lubrication Systems
Radiators and Cooling Fans
High-performance engines like the 2JZ generate significant heat, especially under heavy loads or extended use. Maintaining optimal temperatures is crucial to prevent overheating and ensure reliability.
- Upgraded Radiators: Aluminum radiators, such as those by Mishimoto or Koyo, provide improved cooling efficiency over stock radiators by dissipating heat more effectively.
- High-Performance Fans: Electric cooling fans with adjustable thermostats ensure consistent airflow through the radiator, maintaining stable temperatures even during demanding conditions.
Oil Cooling Enhancements
Oil plays a dual role in lubrication and cooling. For high-power builds, an efficient oil cooling system is critical.
- Air-to-Oil Coolers: These systems use external heat exchangers to dissipate heat, preventing oil degradation.
- Relocation Kits: Oil filter relocation kits improve accessibility and cooling efficiency, particularly in tightly packed engine bays.
Coolant Additives and Maintenance
Adding specialized coolant additives can improve thermal conductivity and reduce hotspots in the cooling system.
- Coolant Flushes: Regular coolant replacements prevent buildup and ensure that the system operates at peak efficiency.
- Water-Methanol Injection: This advanced cooling solution lowers intake temperatures, reducing the risk of detonation and allowing for more aggressive timing and boost settings.
Intercooling for Forced Induction
Intercoolers are integral to managing intake air temperatures in turbocharged applications:
- Front-Mount Intercoolers (FMIC): Larger units dissipate heat more effectively, improving the density of air entering the engine.
- Air-to-Water Intercoolers: Ideal for drag racing setups, offering superior cooling efficiency in short bursts.
Monitoring Systems
Modern cooling systems often integrate monitoring tools to ensure optimal operation:
- Digital Gauges: Real-time temperature readings for oil, coolant, and intake air.
- Temperature Sensors: Advanced systems alert the driver to overheating or irregularities.

Case Studies and Real-World Examples
Popular 2JZ Builds
The 2JZ engine has become a cornerstone in the world of high-performance automotive projects. Here are some standout examples:
- Drag Racing Builds
- Power Output: Exceeding 1,200 horsepower.
- Key Features: Precision Turbochargers, forged internals, standalone ECU systems, and high-octane racing fuel.
- Application: These builds prioritize straight-line acceleration, often running quarter-mile times in the 7-second range.
- Street Performance Builds
- Power Output: 600-800 horsepower.
- Key Features: Upgraded twin turbos, high-flow exhaust systems, and intercooler upgrades.
- Application: Balancing daily drivability with track-ready performance, these builds are perfect for street enthusiasts.
- Time Attack and Circuit Racing Builds
- Power Output: 500-700 horsepower.
- Key Features: Lightweight exhaust systems, advanced cooling solutions, and precision suspension setups.
- Application: Designed for endurance and agility, these builds focus on consistent lap times and thermal efficiency.
Lessons from Tuners
Professional tuners and enthusiasts worldwide have shared valuable insights into optimizing the 2JZ engine:
- Component Synergy: The importance of matching parts, such as turbos, injectors, and ECUs, to avoid inefficiencies.
- Cooling as a Priority: High-power builds often fail due to overheating, making advanced cooling solutions non-negotiable.
- Professional Tuning: Many catastrophic failures are linked to improper tuning. Investing in expert tuning ensures reliability and maximum performance.
Notable Projects and Builders
- Smokey Nagata’s Top Secret Supra: This iconic build famously achieved top speeds exceeding 200 mph with a heavily modified 2JZ.
- Papadakis Racing: Known for pushing the limits of the 2JZ in Formula Drift, showcasing the engine’s versatility and durability.
- Internet Phenomena: YouTube channels and forums frequently highlight 2JZ projects, contributing to its legendary status and providing real-world data for enthusiasts.
Conclusion
The Toyota 2JZ engine is an enduring symbol of automotive engineering excellence, capable of extraordinary power and reliability. From its stock internals to its ability to support extensive modifications, the 2JZ remains a favorite among tuners and performance enthusiasts.
By optimizing factors such as fuel quality, boost pressure, turbocharger selection, engine management, and cooling systems, the 2JZ can achieve unparalleled levels of performance. The insights provided in this guide offer a roadmap for enthusiasts seeking to maximize the potential of their 2JZ-powered builds.
Key takeaways:
- Balance is Key: Each modification should complement the others to achieve harmonious performance.
- Invest in Quality: High-performance parts and professional tuning are essential for both reliability and power.
- Leverage Expertise: Learn from the successes and challenges of experienced tuners and builders.
Whether your goal is a street-ready performance car or a track-dominating monster, the 2JZ engine offers limitless possibilities for those willing to explore its potential. With careful planning, the right components, and dedication, your 2JZ build can truly become a benchmark in the automotive world.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What makes the 2JZ engine so popular among tuners?
The 2JZ engine’s popularity stems from its robust construction, high-performance potential, and reliability. Its cast-iron block, forged internals, and advanced engineering make it capable of handling extreme power levels, often exceeding 1,000 horsepower with proper modifications. Additionally, its aftermarket support and adaptability across various car platforms further enhance its appeal.
How much power can the stock 2JZ-GTE internals handle?
The stock internals of the 2JZ-GTE are known to reliably handle up to 600 horsepower with proper tuning and supporting modifications. Beyond this threshold, upgrading components such as pistons, connecting rods, and the crankshaft becomes necessary to maintain durability and prevent mechanical failure under increased stress.
What are the best turbo upgrade options for the 2JZ engine?
Turbo upgrade options depend on the intended application:
- Single Turbo Upgrades: Ideal for high-power builds, providing simplified plumbing and greater efficiency. Examples include Garrett GTX and Precision Turbo models.
- Upgraded Twin Turbos: Maintain quick spool and balance, such as HKS GT2835 units. The choice should align with your power goals, driving style, and supporting modifications like intercooling and fueling.
How important is professional tuning for a modified 2JZ engine?
Professional tuning is critical for optimizing performance and ensuring reliability. A well-tuned ECU adjusts parameters like air-fuel ratio, ignition timing, and boost pressure, maximizing power while safeguarding against detonation and mechanical damage. DIY tuning or improper settings can lead to catastrophic engine failure, making professional expertise invaluable.
What cooling upgrades are essential for high-performance 2JZ builds?
Cooling is paramount in high-power builds to prevent overheating and maintain engine longevity. Essential upgrades include:
- Aluminum Radiators: Enhance heat dissipation compared to stock units.
- Front-Mount Intercoolers (FMIC): Lower intake air temperatures, critical for turbocharged engines.
- Oil Coolers: Maintain optimal oil temperatures under high stress.
- Water-Methanol Injection: Further reduces intake air temperatures, improving efficiency. These upgrades ensure consistent performance during demanding conditions.