The Toyota 2JZ engine family stands as a hallmark of automotive engineering excellence, revered among car enthusiasts and performance tuners worldwide. Its two primary variants, the 2JZ-GTE and 2JZ-GE, showcase Toyota’s ability to design engines that excel in durability, power, and adaptability. While the 2JZ-GTE is turbocharged and built for high performance, the 2JZ-GE offers a naturally aspirated design suited for smoother, everyday driving.
This detailed comparison explores the stock horsepower and torque figures of these two engines, offering insights into their unique characteristics, capabilities, and potential. Whether you’re a tuner, a Toyota enthusiast, or simply curious about what makes the 2JZ engine family legendary, this analysis will provide a comprehensive understanding of the differences between these powerhouse engines.
Brief History of the 2JZ Engine
The Toyota 2JZ engine family debuted in the early 1990s as part of Toyota’s renowned JZ-series, which replaced the older M-series engines. Built with a focus on durability and versatility, the JZ-series was engineered for high performance and reliability, capable of meeting the demands of both daily driving and motorsports.
2JZ-GE: The Naturally Aspirated Workhorse
Introduced in vehicles like the Toyota Supra MKIV (non-turbo models), Lexus IS300, and Lexus GS300, the 2JZ-GE was designed for smooth power delivery and dependability. Its naturally aspirated setup and high compression ratio made it ideal for drivers who valued efficiency and simplicity over outright speed.
2JZ-GTE: The Turbocharged Performer
Developed as the high-performance counterpart, the 2JZ-GTE took the 2JZ-GE’s robust foundation and enhanced it with sequential twin turbochargers, oil-cooled pistons, and reinforced internals. It was prominently featured in the legendary Toyota Supra MKIV (Twin-Turbo) and select Toyota Aristo models. The 2JZ-GTE quickly became a tuner favorite due to its immense power potential and ability to handle significant modifications.
Why the 2JZ Stands Out
- Durable Construction: Both engines share a cast-iron block, renowned for its strength and resistance to high-pressure environments.
- Global Fanbase: The 2JZ engine family gained cult status, supported by appearances in motorsports, movies like The Fast and the Furious, and a strong aftermarket ecosystem.
- Performance Legacy: The 2JZ’s reliability and power delivery have made it a benchmark for inline-six engines, influencing the development of competitors’ offerings.
Core Specifications
The 2JZ-GE and 2JZ-GTE, while sharing the same 3.0-liter inline-six foundation, diverge significantly in terms of their design, power output, and intended use. Below is a detailed breakdown of their core specifications.
2JZ-GE: Naturally Aspirated
- Engine Displacement: 2,997 cc (3.0 liters)
- Power Output:
- 215–230 horsepower @ 5,800–6,000 rpm
- Torque:
- 209–220 lb-ft @ 4,800–5,800 rpm
- Compression Ratio: 10.5:1
- Fuel System: Sequential Electronic Fuel Injection (EFI)
- Cylinder Head: Aluminum with optimized intake flow for naturally aspirated performance
- Applications:
- Toyota Supra (Non-Turbo, MKIV)
- Lexus IS300
- Lexus GS300
2JZ-GTE: Turbocharged
- Engine Displacement: 2,997 cc (3.0 liters)
- Power Output:
- Japanese Domestic Market (JDM): ~276 horsepower @ 5,600 rpm (limited by “Gentlemen’s Agreement”)
- Export Models: 320 horsepower @ 5,600 rpm
- Torque:
- JDM: 318 lb-ft @ 4,000 rpm
- Export: 315 lb-ft @ 4,000 rpm
- Compression Ratio: 8.5:1
- Forced Induction: Sequential twin turbochargers
- Fuel System: Sequential EFI with upgraded injectors for higher fuel delivery
- Cylinder Head: Aluminum with enhanced intake flow for turbocharging
- Applications:
- Toyota Supra MKIV (Twin Turbo)
- Toyota Aristo (JZS147/161)
Comparison Table 2JZ-GTE and 2JZ-GE
| Specification | 2JZ-GE | 2JZ-GTE |
| Displacement | 2,997 cc | 2,997 cc |
| Power (hp) | 215–230 | 276 (JDM), 320 (Export) |
| Torque (lb-ft) | 209–220 | 318 (JDM), 315 (Export) |
| Compression Ratio | 10.5:1 | 8.5:1 |
| Forced Induction | None | Sequential Twin Turbochargers |
| Fuel System | Sequential EFI | Sequential EFI with upgrades |
| Applications | Supra, IS300, GS300 | Supra (Turbo), Aristo |
The specifications highlight the 2JZ-GE’s efficient and straightforward design versus the 2JZ-GTE’s performance-oriented engineering. The inclusion of turbocharging, lower compression ratio, and internal reinforcements make the GTE far more capable in high-performance scenarios.
Internal and Design Differences
While both the 2JZ-GE and 2JZ-GTE share the same cast-iron block and basic architecture, their internal components and design philosophies differ significantly. These differences enable the 2JZ-GTE to handle the immense stresses of turbocharging, while the 2JZ-GE is optimized for naturally aspirated performance.
Forced Induction vs. Naturally Aspirated Design
- 2JZ-GE:
- The 2JZ-GE operates as a naturally aspirated engine, relying on higher compression (10.5:1) to generate power efficiently without forced induction.
- Its intake and exhaust designs are optimized for smoother airflow, making it a dependable choice for daily driving or light performance applications.
- 2JZ-GTE:
- Equipped with sequential twin turbochargers, the 2JZ-GTE is designed to deliver significant power increases. The lower compression ratio (8.5:1) accommodates higher boost levels without risking engine knock.
- The turbocharging system allows for minimal turbo lag at lower RPMs and high power delivery at higher RPMs, making it suitable for performance-focused applications.
Internal Components
- 2JZ-GE:
- Features standard cast pistons and connecting rods, which are sufficient for naturally aspirated power levels.
- While not designed for forced induction, many tuners have successfully turbocharged the GE with upgraded internals.
- 2JZ-GTE:
- Built with reinforced internals, including:
- Oil-cooled pistons: To manage the high thermal stresses of turbocharging.
- Oil squirters: Located at the base of the cylinders to ensure adequate cooling of the pistons.
- Heavy-duty connecting rods and crankshaft: Designed to withstand the increased stress from forced induction.
- These enhancements make the GTE capable of handling up to 600 hp on stock internals with proper tuning.
- Built with reinforced internals, including:
Cylinder Head Design
- 2JZ-GE:
- The aluminum cylinder head features a simpler port design, emphasizing efficiency and smooth airflow for naturally aspirated performance.
- 2JZ-GTE:
- The cylinder head includes larger intake and exhaust ports, optimized for high airflow demanded by turbocharged engines.
- Improved valvetrain components and a more aggressive cam profile ensure optimal performance under boost.
Fuel and Cooling Systems
- 2JZ-GE:
- Uses standard sequential EFI and a conventional cooling system sufficient for naturally aspirated operation.
- 2JZ-GTE:
- Features upgraded injectors to support the higher fuel delivery needs of turbocharging.
- The GTE also includes an intercooler to cool compressed air from the turbochargers, enhancing performance and preventing detonation.
Summary of Design Enhancements
| Feature | 2JZ-GE | 2JZ-GTE |
| Compression Ratio | 10.5:1 | 8.5:1 |
| Pistons | Standard Cast | Oil-Cooled |
| Connecting Rods | Standard | Reinforced |
| Turbocharging | None | Sequential Twin Turbochargers |
| Cooling System | Standard | Intercooler, Oil Squirters |
| Cylinder Head Design | Standard Flow Design | Optimized for High Airflow |
The 2JZ-GTE’s robust internals and advanced engineering allow it to thrive under turbocharged conditions, whereas the 2JZ-GE focuses on efficiency and simplicity, making it a strong base for enthusiasts who value reliability or plan future upgrades.
Performance Analysis
The 2JZ-GE and 2JZ-GTE deliver significantly different performance experiences due to their respective naturally aspirated and turbocharged designs. This section analyzes their stock horsepower and torque figures, throttle response, and driving characteristics.
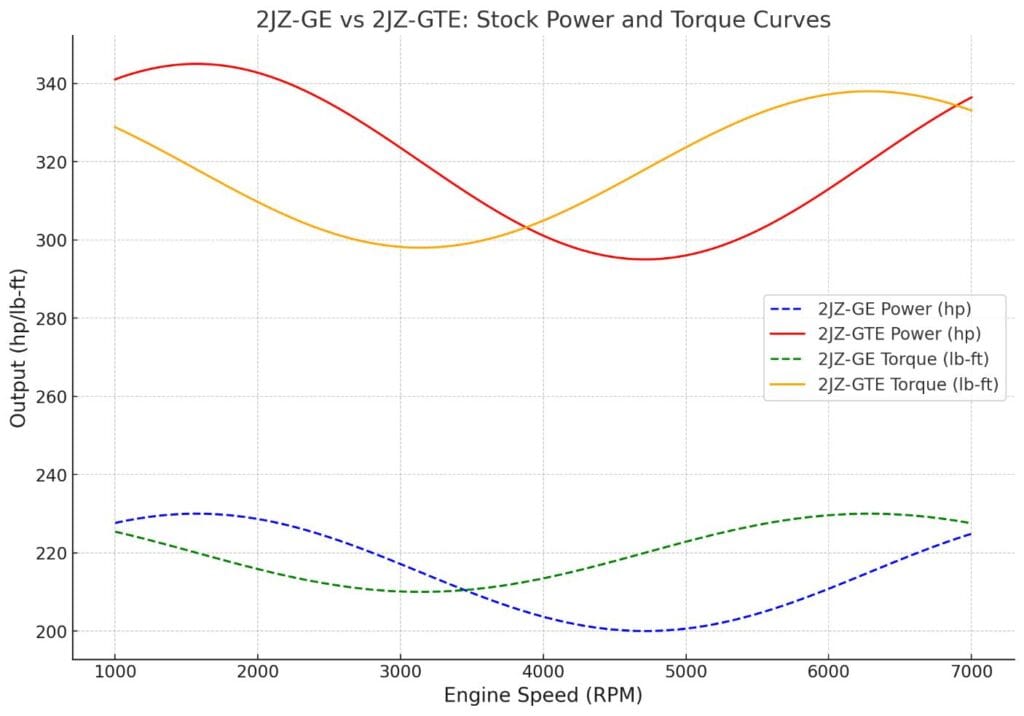
Horsepower and Torque Comparison
- 2JZ-GE (Naturally Aspirated):
- Horsepower: 215–230 hp @ 5,800–6,000 rpm
- Torque: 209–220 lb-ft @ 4,800–5,800 rpm
- Performance Characteristics:
- Linear power delivery.
- Smoother throttle response ideal for daily driving.
- Lack of forced induction means no turbo lag but limited peak power.
- 2JZ-GTE (Turbocharged):
- Horsepower:
- JDM: ~276 hp (official rating due to “Gentlemen’s Agreement”).
- Export Models: 320 hp @ 5,600 rpm.
- Torque:
- JDM: 318 lb-ft @ 4,000 rpm.
- Export Models: 315 lb-ft @ 4,000 rpm.
- Performance Characteristics:
- Explosive power delivery due to twin turbos.
- Minimal turbo lag from sequential setup.
- Higher torque output ensures stronger acceleration and performance under load.
- Horsepower:
Throttle Response and Driving Feel
- 2JZ-GE:
- The naturally aspirated engine offers immediate throttle response without delays or surges.
- Smooth and predictable power curve makes it user-friendly for drivers new to performance engines.
- Suitable for consistent driving conditions, such as city commutes or long highway journeys.
- 2JZ-GTE:
- Turbochargers introduce slight turbo lag at low RPMs but deliver a dramatic surge of power as boost builds.
- More suited for spirited driving or track performance, where the engine operates in higher RPM ranges.
- Superior for overtaking and high-speed acceleration.
Practical Applications
- 2JZ-GE:
- Ideal for vehicles with a focus on reliability and fuel efficiency.
- Often chosen for daily drivers or projects where simplicity and cost-effectiveness are priorities.
- 2JZ-GTE:
- Designed for performance-oriented applications, such as motorsports or high-speed cruising.
- Widely used in drag racing, drifting, and tuning due to its incredible stock power and tuning potential.
Real-World Performance Metrics
| Engine Variant | 0-60 mph Time | Top Speed | Quarter Mile (Stock) |
| 2JZ-GE | ~7.5 seconds | ~140 mph | ~15.5 seconds |
| 2JZ-GTE | ~5.0 seconds | ~155 mph | ~13.5 seconds |
Reliability Under Stock Conditions
- 2JZ-GE:
- Renowned for long-term durability.
- Minimal stress on internals due to lack of forced induction.
- Requires basic maintenance, making it an affordable option.
- 2JZ-GTE:
- Equally reliable under stock conditions, thanks to reinforced internals.
- Turbocharging adds thermal and mechanical stress but remains manageable with regular maintenance.
- Higher fuel consumption compared to the GE due to increased performance.
The 2JZ-GTE excels in raw performance and acceleration, making it the clear choice for enthusiasts seeking high-speed thrills. On the other hand, the 2JZ-GE provides balanced, reliable performance suitable for daily use and less demanding scenarios.
Stock Power Outputs in Different Markets
The power outputs of the 2JZ-GE and 2JZ-GTE vary depending on the market due to regional regulations, consumer preferences, and Toyota’s compliance with the industry agreements of the time. This section highlights the nuances of their stock performance across different regions.
The Japanese Domestic Market (JDM)
- 2JZ-GE:
- Power: ~220 hp @ 5,800 rpm
- Torque: ~210 lb-ft @ 4,800 rpm
- Features a balanced performance for non-turbo variants, catering to consumers valuing smooth driving and fuel efficiency.
- 2JZ-GTE:
- Power: Officially rated at 276 hp @ 5,600 rpm.
- This figure aligns with the “Gentlemen’s Agreement,” a pact among Japanese automakers to limit advertised horsepower to 276 hp.
- Torque: ~318 lb-ft @ 4,000 rpm.
- Real-world output often exceeded the stated 276 hp, with some dyno tests indicating closer to 300 hp or more in stock form.
- Power: Officially rated at 276 hp @ 5,600 rpm.
Export Markets (North America and Europe)
- 2JZ-GE:
- Power: ~215 hp @ 5,800 rpm (slightly lower than JDM models due to emissions controls).
- Torque: ~209 lb-ft @ 4,800 rpm.
- Export versions of the GE were tuned for emissions compliance and fuel economy, making them slightly less powerful than their JDM counterparts.
- 2JZ-GTE:
- Power: 320 hp @ 5,600 rpm.
- Torque: 315 lb-ft @ 4,000 rpm.
- Free from the constraints of the “Gentlemen’s Agreement,” export versions were marketed with their true performance figures, giving consumers a more transparent view of the GTE’s capabilities.
Factors Influencing Regional Power Outputs
- Regulatory Standards:
- JDM engines adhered to strict domestic power agreements and emissions regulations.
- Export models, particularly for the U.S., faced stringent emissions requirements but had more leeway to advertise actual horsepower figures.
- Fuel Quality:
- Higher octane ratings in Japan (commonly 98 RON) allowed engines to perform optimally.
- In export markets with lower octane fuels, performance was slightly adjusted to maintain reliability.
- Market Positioning:
- Toyota positioned the 2JZ-GE and 2JZ-GTE differently depending on market demand, emphasizing performance in export regions and reliability in domestic markets.
Comparison of Stock Power Outputs
| Market | 2JZ-GE Power (hp) | 2JZ-GE Torque (lb-ft) | 2JZ-GTE Power (hp) | 2JZ-GTE Torque (lb-ft) |
| JDM | ~220 | ~210 | ~276 | ~318 |
| Export (NA/EU) | ~215 | ~209 | ~320 | ~315 |
Real-World Implications
- JDM Models:
- While officially limited in power, the 2JZ-GTE in JDM vehicles often delivered performance exceeding advertised specifications.
- Export Models:
- Transparency in marketing allowed export models to highlight the 2JZ-GTE’s superiority in power and torque, solidifying its appeal in global markets.
The variations in stock power figures between markets reflect Toyota’s ability to adapt to regional demands while maintaining the reliability and performance the 2JZ engines are known for.
Modification Potential
The 2JZ-GE and 2JZ-GTE are celebrated for their tuning potential, with enthusiasts pushing both engines far beyond their stock power figures. This section explores their modification capabilities and limitations.
2JZ-GE: Unlocking Performance
While the 2JZ-GE was designed as a naturally aspirated engine, its robust construction makes it a suitable candidate for forced induction and other performance upgrades.
- Turbocharging a 2JZ-GE:
- Potential Gains: A properly turbocharged 2JZ-GE can achieve 400–500 hp with upgraded internals.
- Required Modifications:
- Reinforced pistons, rods, and crankshaft.
- Upgraded fuel injectors and fuel pump.
- Aftermarket standalone ECU for precise tuning.
- A thicker head gasket to lower the effective compression ratio.
- Naturally Aspirated Builds:
- Focus on higher compression, ported cylinder heads, and aggressive camshafts.
- Gains are more modest, typically resulting in around 250–270 hp.
- Limitations:
- The stock internals of the 2JZ-GE are not designed for the stresses of high-boost turbocharging.
- Cooling upgrades are essential to handle increased heat generation.
2JZ-GTE: The Tuner’s Dream
The 2JZ-GTE is widely regarded as one of the best platforms for extreme horsepower builds, capable of reaching 1,000+ hp with the right upgrades.
- Stock Internal Capabilities:
- The 2JZ-GTE can reliably handle up to 600 hp on stock internals with proper tuning.
- Sequential twin turbos can be retained or replaced with a single large turbo for simplified plumbing and higher peak power.
- Popular Modifications:
- Single Turbo Conversion: Upgrading to a single large turbo (e.g., Garrett or BorgWarner) for power outputs exceeding 800 hp.
- Fuel System Upgrades: High-flow fuel injectors, dual fuel pumps, and upgraded fuel rails to support extreme power levels.
- Forged Internals: Pistons, rods, and crankshaft upgrades to handle the stress of 1,000+ hp builds.
- Standalone ECU: Precise engine management for advanced tuning and reliability.
- Supporting Mods: Intercooler upgrades, high-flow exhaust systems, and custom intake manifolds.
- Tuning Potential:
- With aftermarket components, 2JZ-GTE engines have been known to exceed 1,500 hp, making them a staple in drag racing and high-speed applications.
Comparison of Modification Potential
| Aspect | 2JZ-GE | 2JZ-GTE |
| Stock Power Handling | ~250–300 hp | ~600 hp |
| Forced Induction | Requires internal upgrades | Built for turbocharging |
| Tuning Limit | ~400–500 hp (modified) | 1,000+ hp (modified) |
| Cost of Modification | Generally lower | Higher due to advanced internals |
Real-World Applications
- 2JZ-GE Builds:
- Affordable entry into the 2JZ world, ideal for enthusiasts on a budget.
- Common in sleeper builds, where the goal is to surprise others with unexpected performance.
- 2JZ-GTE Builds:
- The go-to choice for high-performance applications, including drag racing, drifting, and top-speed runs.
- Ideal for enthusiasts seeking extreme horsepower levels without compromising reliability.
The modification potential of the 2JZ-GTE makes it a legend in the tuning community, while the 2JZ-GE provides a more accessible platform for creative builds. Both engines offer a unique path to performance, depending on goals and budgets.
Comparison with Competitors
The 2JZ-GE and 2JZ-GTE, as part of Toyota’s legendary JZ series, often find themselves compared to other high-performance engines. Chief among these rivals is Nissan’s RB26DETT, the turbocharged inline-six engine that powers the Nissan Skyline GT-R. Here’s a closer look at how the 2JZ engines stack up against their most notable competitors.
Nissan RB26DETT
- Specifications:
- Engine: 2.6L inline-six, twin-turbocharged.
- Power: 276 hp (JDM) and ~320 hp (actual output in many tests).
- Torque: 260 lb-ft @ 4,400 rpm.
- Compression Ratio: 8.5:1.
- Comparison with 2JZ-GTE:
- Both engines feature twin-turbo setups and robust internals, but the 2JZ-GTE’s larger displacement (3.0L) provides a clear torque advantage (~318 lb-ft vs. 260 lb-ft).
- The RB26DETT is highly regarded for its high-revving nature, with a redline around 8,000 RPM compared to the 2JZ-GTE’s ~7,000 RPM.
- In tuning potential, both engines are capable of exceeding 1,000 hp, but the 2JZ-GTE is often praised for its simpler aftermarket support and easier maintenance.
BMW S54
- Specifications:
- Engine: 3.2L inline-six, naturally aspirated.
- Power: 333 hp @ 7,900 rpm (Euro-spec M3 E46).
- Torque: 262 lb-ft @ 4,900 rpm.
- Compression Ratio: 11.5:1.
- Comparison with 2JZ-GE:
- The S54 delivers more power and torque than the 2JZ-GE in its stock naturally aspirated configuration, thanks to advanced technology like individual throttle bodies.
- The 2JZ-GE, however, offers greater modification potential, especially for forced induction builds.
- The 2JZ-GE is more robust for long-term reliability, as the S54 is known for issues like rod bearing failures under high stress.
Mitsubishi 4G63
- Specifications:
- Engine: 2.0L inline-four, turbocharged.
- Power: 276 hp (Evo IX) and up to ~400 hp in some stock variants.
- Torque: ~289 lb-ft @ 3,500 rpm.
- Compression Ratio: 8.8:1.
- Comparison with 2JZ-GTE:
- The 2JZ-GTE outclasses the 4G63 in terms of displacement, torque, and high-power capability.
- The 4G63’s compact size makes it more suited for lightweight vehicles like the Mitsubishi Lancer Evolution, whereas the 2JZ-GTE is ideal for heavier sports cars like the Toyota Supra.
Chevrolet LS-Series V8s
- Specifications:
- Engine: 5.7L–6.2L V8, naturally aspirated or supercharged.
- Power: 350–650 hp (varies by model).
- Torque: 350–650 lb-ft.
- Compression Ratio: ~10.0:1.
- Comparison with 2JZ-GTE:
- LS engines provide greater displacement and torque in stock form, making them dominant in drag racing.
- The 2JZ-GTE is favored for its inline-six design, which allows for easier packaging in certain vehicles and smoother power delivery.
- Tuning potential is comparable, but the LS series often achieves high horsepower at a lower cost.
Audi 2.5L TFSI
- Specifications:
- Engine: 2.5L inline-five, turbocharged.
- Power: 400 hp @ 7,000 rpm (RS3).
- Torque: 354 lb-ft @ 5,000 rpm.
- Compression Ratio: 10.0:1.
- Comparison with 2JZ-GTE:
- The Audi engine’s modern turbocharging technology allows it to achieve higher stock power, but the 2JZ-GTE’s robust design makes it more suitable for extreme tuning.
- The 2.5L TFSI excels in lightweight, AWD applications, while the 2JZ-GTE is more versatile across different platforms.
Summary Comparison Table
| Engine | Displacement | Power (hp) | Torque (lb-ft) | Tuning Potential | Applications |
| 2JZ-GTE | 3.0L I6 | 276–320 | 315–318 | 1,000+ hp | Toyota Supra, Aristo |
| RB26DETT | 2.6L I6 | 276+ | ~260 | 1,000+ hp | Nissan Skyline GT-R |
| S54 | 3.2L I6 | 333 | 262 | ~400 hp (NA) | BMW M3 (E46) |
| 4G63 | 2.0L I4 | 276+ | ~289 | ~800 hp | Mitsubishi Lancer Evolution |
| LS-Series V8s | 5.7L+ V8 | 350–650 | 350–650 | 1,000+ hp | Chevrolet Corvette, Camaro |
| 2.5L TFSI | 2.5L I5 | 400 | 354 | ~600 hp | Audi RS3, TT RS |
Verdict: The 2JZ Legacy
The 2JZ-GTE shines for its balance of reliability, tuning potential, and performance in high-power applications, often outclassing competitors in the long-term versatility department. The 2JZ-GE, while less powerful, offers an accessible entry point for enthusiasts and a reliable base for modification.

Use Cases
The versatility and reliability of the 2JZ-GE and 2JZ-GTE have made them favorites in various automotive scenarios, ranging from daily drivers to high-performance motorsports. Here, we explore their ideal applications and the benefits they offer in real-world use cases.
2JZ-GE: Practicality Meets Affordability
The 2JZ-GE is an excellent option for drivers seeking reliable, naturally aspirated performance with potential for light modifications.
- Daily Drivers:
- Smooth power delivery and lower maintenance costs make the 2JZ-GE ideal for everyday vehicles like the Lexus IS300 and GS300.
- Fuel efficiency is better compared to its turbocharged sibling, making it economical for city and highway use.
- Beginner Projects:
- Affordable entry-level engine for enthusiasts new to performance tuning.
- Great platform for learning about engine modification and maintenance.
- Light Performance Builds:
- Naturally aspirated builds with upgraded cams, ported cylinder heads, and custom exhaust systems can enhance power and driving enjoyment without significant investment.
2JZ-GTE: Performance-Oriented Applications
The 2JZ-GTE’s robust design and turbocharging capabilities make it the go-to choice for enthusiasts looking for high power and versatility.
- Motorsports:
- A staple in drag racing, capable of delivering over 1,000 hp with appropriate modifications.
- Commonly used in drifting due to its high torque and responsive power delivery.
- High-Performance Street Builds:
- Ideal for sports cars like the Toyota Supra MKIV, offering exhilarating acceleration and top-end performance.
- Widely swapped into vehicles for sleeper builds, where its power transforms unsuspecting platforms.
- Tuning and Customization:
- With a vast aftermarket ecosystem, the 2JZ-GTE is easily customized for specific needs, from time attack builds to high-speed highway racers.
- Popular in engine swaps for vehicles ranging from Nissan 240SXs to BMW chassis.
Comparison of Use Cases
| Use Case | 2JZ-GE | 2JZ-GTE |
| Daily Driving | Excellent reliability, lower cost | High performance but less efficient |
| Motorsports | Limited application | Dominant in drag and drift racing |
| Tuning Potential | Moderate (~400 hp) | Extreme (~1,500+ hp) |
| Affordability | Budget-friendly | Higher initial cost, but scalable |
| Engine Swaps | Common for cost-effective builds | Preferred for high-power builds |
Real-World Examples
- 2JZ-GE in Sleeper Builds:
- A turbocharged 2JZ-GE in a Toyota Camry or Lexus SC300 can surprise competitors on the street or track.
- 2JZ-GTE in Competitive Racing:
- Frequently seen in professional drift championships, where its torque and reliability under stress are crucial.
- Show Cars:
- Both engines are featured in custom builds, showcasing polished engine bays and extreme modifications that highlight their engineering excellence.
The 2JZ-GE thrives in scenarios where reliability, affordability, and ease of maintenance are priorities. Meanwhile, the 2JZ-GTE dominates in high-performance applications, making it a legendary choice for motorsports and extreme builds.
Community Insights
The 2JZ-GE and 2JZ-GTE have a strong presence in the automotive community, with countless discussions on forums, YouTube channels, and social media platforms. These engines have earned their reputation not only for their performance but also for their reliability and tunability. Here, we dive into the real-world opinions and experiences of enthusiasts.
Enthusiast Forums
- Supra Forums (2JZ-GTE):
- Strengths: Regularly praised for its ability to handle high horsepower with minimal modifications.
- Discussions: Common topics include single-turbo conversions, tuning strategies, and the best ECU options.
- Quote: “The 2JZ-GTE is the engine that keeps giving; even after 20+ years, it’s still outclassing modern competitors.”
- Club Lexus (2JZ-GE):
- Strengths: Valued for its reliability and simplicity.
- Discussions: Topics often focus on cost-effective ways to add power, such as turbocharging the GE with minimal upgrades.
- Quote: “You don’t need to go GTE to have fun—a turbo GE build can surprise you!”
Social Media and YouTube
- YouTube:
- Popular Videos: Videos comparing the two engines, showcasing builds, and performing dyno tests consistently attract millions of views.
- Example: “2JZ-GE vs. 2JZ-GTE: Which Is Right for You?” highlights the pros and cons of each engine for different types of builds.
- Social Media Groups:
- Active communities on Facebook and Reddit provide advice, share success stories, and discuss modifications.
- Memes and posts often reference the iconic status of the 2JZ-GTE, comparing it to newer engines with humor and nostalgia.
User Experiences
- 2JZ-GE Owners:
- Many praise the engine for being a great starting point for projects.
- Turbocharged 2JZ-GE builds are described as “budget-friendly GTE alternatives” that still pack a punch.
- 2JZ-GTE Owners:
- Universally admired for its incredible power potential and durability.
- Described as a “must-have” for those pursuing high-horsepower goals, with owners often pushing 1,000+ hp.
Community-Based Knowledge
- Strengths of the 2JZ Family:
- Both engines are praised for their robust design, with terms like “bulletproof” frequently used to describe their reliability.
- The availability of aftermarket parts ensures these engines remain viable choices for builds.
- Common Challenges:
- For the 2JZ-GE, the cost of turbocharging and upgrading internals can escalate quickly.
- For the 2JZ-GTE, sourcing genuine parts like turbos or injectors can be expensive due to high demand.
Practical Advice from the Community
| Advice | 2JZ-GE | 2JZ-GTE |
| Best Modifications | Turbo kits with proper tuning | Single-turbo upgrades |
| Maintenance Tips | Regular timing belt inspections | Monitor boost levels carefully |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Ideal for budget builds | Higher initial investment, better ROI |
| Aftermarket Support | Strong, but limited for high power | Extensive and well-established |
Community Verdict
- The 2JZ-GE is the community’s recommendation for beginners or those on a budget, offering flexibility and reliability without breaking the bank.
- The 2JZ-GTE, on the other hand, is hailed as the ultimate engine for high-performance builds, with enthusiasts calling it “legendary” for its unmatched tuning potential and proven track record.
Complete Comparison Table: 2JZ-GE and 2JZ-GTE
| Feature | 2JZ-GE (Naturally Aspirated) | 2JZ-GTE (Turbocharged) |
| Engine Displacement | 2,997 cc (3.0 liters) | 2,997 cc (3.0 liters) |
| Power (Stock) | 215–230 hp @ 5,800–6,000 rpm | 276 hp (JDM) / 320 hp (Export) @ 5,600 rpm |
| Torque (Stock) | 209–220 lb-ft @ 4,800–5,800 rpm | 318 lb-ft (JDM) / 315 lb-ft (Export) @ 4,000 rpm |
| Compression Ratio | 10.5:1 | 8.5:1 |
| Induction System | Naturally Aspirated | Sequential Twin Turbochargers |
| Cylinder Head Design | Aluminum, optimized for naturally aspirated flow | Aluminum, optimized for turbocharged flow |
| Fuel System | Sequential EFI | Sequential EFI with larger injectors |
| Pistons | Standard cast | Oil-cooled, reinforced |
| Internals (Stock) | Standard rods and crankshaft | Reinforced rods, crankshaft, and oil squirters |
| Cooling System | Conventional radiator | Includes an intercooler and advanced oil cooling system |
| Market Applications | Toyota Supra (Non-Turbo), Lexus IS300, Lexus GS300 | Toyota Supra (Turbo), Toyota Aristo |
| Stock 0-60 mph Time | ~7.5 seconds | ~5.0 seconds |
| Stock Quarter-Mile Time | ~15.5 seconds | ~13.5 seconds |
| Tuning Potential | ~400–500 hp with modifications | 1,000+ hp with modifications |
| Best Use Cases | Daily driving, fuel efficiency, light performance builds | Drag racing, drifting, high-performance builds |
| Maintenance Complexity | Low | Moderate to high |
| Cost of Modification | Relatively low | Higher, due to advanced internals |
| Aftermarket Support | Moderate | Extensive |
| Popularity in Swaps | Common for budget-friendly builds | Extremely popular for high-performance swaps |
Conclusion
The Toyota 2JZ engine family, encompassing the naturally aspirated 2JZ-GE and the turbocharged 2JZ-GTE, represents a pinnacle of automotive engineering that continues to captivate enthusiasts worldwide. These engines have become legends, not only for their stock performance but also for their immense tuning potential and reliability.
Key Takeaways
- 2JZ-GE:
- Designed for smooth, reliable performance in naturally aspirated form.
- Delivers 215–230 hp and 209–220 lb-ft of torque in stock configuration.
- Ideal for daily driving and budget-friendly projects, with moderate tuning capabilities.
- 2JZ-GTE:
- Turbocharged for exceptional power, producing 276–320 hp and 315–318 lb-ft of torque.
- Built with reinforced internals, making it a top choice for high-performance applications and extreme horsepower builds.
- A tuner’s dream, capable of handling over 1,000 hp with proper modifications.
Community Consensus
- Enthusiasts praise the 2JZ-GTE for its versatility in high-performance builds, often referring to it as “bulletproof.”
- The 2JZ-GE is celebrated for its reliability and affordability, providing a solid foundation for newcomers to engine modification.
Final Thoughts
Whether you’re drawn to the naturally aspirated simplicity of the 2JZ-GE or the turbocharged prowess of the 2JZ-GTE, both engines stand as testaments to Toyota’s engineering excellence. They offer pathways to performance that cater to both budget-conscious beginners and seasoned tuners alike.
With a vibrant community and an ever-expanding aftermarket, the 2JZ engine family continues to thrive as a symbol of automotive passion and innovation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) 2JZ-GE vs. 2JZ-GTE
What are the main differences between the 2JZ-GE and the 2JZ-GTE?
The 2JZ-GE is a naturally aspirated engine designed for smooth power delivery, reliability, and fuel efficiency. It produces 215–230 horsepower and 209–220 lb-ft of torque. The 2JZ-GTE, on the other hand, is turbocharged with a sequential twin-turbo system, delivering 276 horsepower (JDM) or 320 horsepower (export) and up to 318 lb-ft of torque. The 2JZ-GTE features reinforced internals, lower compression (8.5:1), and enhanced cooling systems, making it better suited for high-performance applications.
Can I turbocharge a 2JZ-GE engine?
Yes, the 2JZ-GE can be turbocharged, but it requires significant modifications to handle the increased stress. Key upgrades include:
- Forged pistons and connecting rods.
- A thicker head gasket to lower compression.
- Upgraded fuel injectors, fuel pump, and standalone ECU for proper tuning.
- A high-quality turbo kit. While it can deliver similar power to a 2JZ-GTE with these modifications, the cost and effort often lead enthusiasts to swap in a 2JZ-GTE instead.
How much horsepower can the stock 2JZ-GTE handle?
The 2JZ-GTE is renowned for its strength and durability. On stock internals, it can reliably handle up to 600 horsepower with proper tuning and supporting modifications, such as an upgraded fuel system and turbochargers. With reinforced internals, the engine can exceed 1,000 horsepower, making it one of the most sought-after platforms for extreme builds.
Which engine is better for a daily driver: 2JZ-GE or 2JZ-GTE?
For daily driving, the 2JZ-GE is the better option. Its naturally aspirated design provides smooth, predictable power delivery and better fuel efficiency, making it more practical for everyday use. The 2JZ-GTE, while more powerful, may be less fuel-efficient and requires more maintenance, especially when modified for high-performance use.
What are the best cars to swap a 2JZ-GTE into?
The 2JZ-GTE is a versatile engine that has been swapped into a wide variety of vehicles. Popular choices include:
- Toyota Supra (non-turbo models): The natural upgrade path for Supra enthusiasts.
- Nissan 240SX/Silvia: A lightweight chassis that benefits from the power of the 2JZ-GTE.
- BMW E30/E36: European cars that pair well with the inline-six layout.
- Mazda RX-7 (FD): For unique builds that combine rotary chassis with inline-six power. Its relatively compact size and robust aftermarket support make it a favorite for custom performance projects.